While choosing Ethernet cable for your home, you may face some unknown terms like Megabits, Cats, and lines. That’s why it is vital for you to know about each Ethernet wires’ features and uses. And you also have to know about the difference between Category 1, Category 2, Category 3, Category 4, Category 5, Category 5e, Category 6, Category 7, Category 8 cables. This article will help you in this case by letting you know about all these things correctly.
Know Your Ethernet Cables:
Ethernet Cables are used to connect electric devices with networks for home purposes, business, and office usages. If you want to buy an internet line for your home usage, then knowing about the right network cable or LAN Cable of grade Cat 5, Cat 6, and Cat 7, is very much important for you. These are usually twisted wires that are more effective in increasing the network speeds.
You can get these LAN cables available in different length similar to the patch cables. The length of the long Ethernet wire is usually up to 75 meters. These types of LAN cables have four Ethernet ports that allow you to use your gadget directly. You can use them to connect network devices with routers, PCs, etc. However if an Ethernet wire doesn’t have good quality or the length of the Wire is too long, you can’t get quality network signals. These cables have the highest 100 m lengths.
Usually, Ethernet cable looks like a traditional phone cable. Though, both cables come in similar shapes, the size of the Ethernet cable is thicker. Moreover, it contains more wires (Contains eight wires).
How to Choose a Right Ethernet cable:
First, check your home network speed. Whether you have gigabit internet (1Gbps), you can use the Ethernet cable. In case you are dealing with a slow network connection like 10 or 20 megabits per second, you can use a category 5 or upgraded version.
If you are not aware of your internet subscription’s actual speed, connect your PC to the modem. After connecting it, you can check the internet speed. Whether your subscription can support only 50Mbps downloads, then you should not buy the Ethernet cables. After buying the right cable for you, you need to adjust the network speed. When you transfer big files between computers or stream videos of high bandwidths, an Ethernet cable can help you the most.
Nowadays, the routers have very high speed. That’s why you must need advanced cable. However, you should choose a right LAN cable of recent versions so that it can offer excellent speed. These cables are capable of working with high-end network devices.
What does the term ‘Cat’ mean?
The term ‘cat’ means category. For example, cat5, cat 5e, cat6, cat7 wires imply Category5, Category 5e, Category6, and Category7 cables.
Ethernet cable types
Category 2
In the late 1980s, people used coaxial cables to connect devices with the networks. These cables known as Category 1 cable or voice-grade cable. These wires are twisted to decrease cross-talk and are covered in a plastic jacket. Category 1 wire can carry a 10 KHz signal.
Cat 3
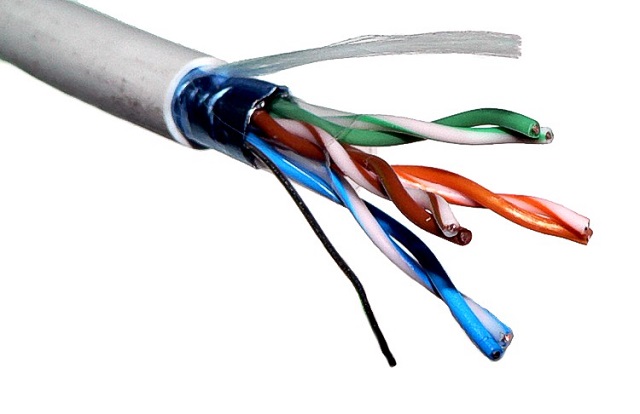
We know these ones as station wires. These cables were also known as VG or voice-grade. These are un-shielded twisted pair cables that are used on the telephone.
Cat 5e
It is known as CAT5e as Category 5e or Category 5 Enhanced. Generally, using routers, we can get network speeds of 10 or 100 megabits per second. People prefer to use Gigabit Ethernet routers in recent times. Compared to the older version, this Category 5e offers up to 10 times faster speed. All old and new cables support Gigabit Ethernet. The old version of the category 5e cable is no longer a recognized as a standard one. But still, it can support gigabit speeds. The cable is used to carry the signals of video and telephony. This 24-gauge twisted pair wires support Gigabit networks.
Cat 6
The wire supports both Category 3 and Category 5/5e cable standards. Most people prefer to use the Category 6 cable as it is a standardized twisted pair wire. However, a few users complain that these ones are hard to install and use. It has four twisted pairs of copper wire.
The size of the cables is 23 AWG gauge. Category 6 lines offer 250 MHz performance because of using a nylon spline in the wiring. This handy cable gives Near-End Cross-talk (NEXT) in the transmission. Besides, it assists in improving the ELFEXT, RL, and IL. Here, ELFEXT, RL, IL stands for Equal-Level Far-End Cross-talk, Return Loss, and Insertion Loss, respectively.
For the Category 6 cable, the network can support only 55 meters (180 ft) length while used for 10GBASE-T. The wires can be twisted to insulate it more than previous times. These cables can support the Gigabit Ethernet segments up to 100 m. You can use 10-Gigabit networks in a limited distance. When you work on a system using category6 wire, you will get lesser errors.
Cat 6a
Here, “a” in Cat 6a means “augmented.” These cables are advanced from the Cat 6 versions, as these cables support twice of the maximum bandwidth. These cables can maintain higher transmission speeds over longer cable lengths.
Cat 7
This type of wire can typically support 10 Gbps. It can transmit up to 40 GB at 50 meters and 100 GB at 15 meters. Here, you can get a new “Class F” cabling that can support up to 600 MHz frequencies. You can share data signals from the routers to the devices by using the Category 7 cable. But it needs frequencies up to 600 MHz Designers make this type of wire in such a way so that it can offer a Gigabit Ethernet over 100 m length.
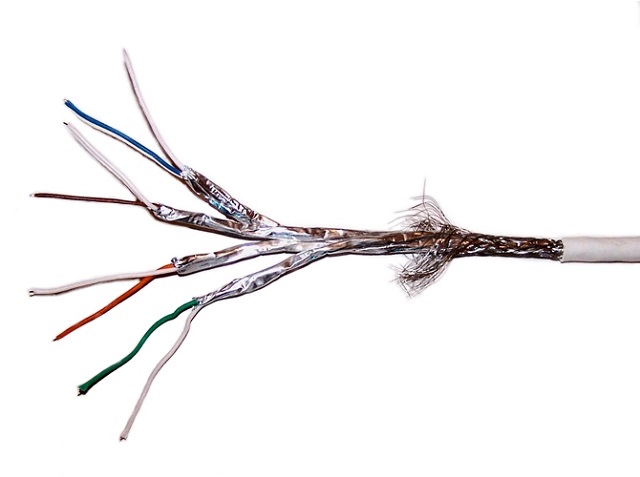
But you should not use this type of wire for telecommunications. You can not get shielding from cross-talk and interference in both cases. You can use this wire in data centers and large enterprise networks. This cable has 600Mhz/10Gbps/100m and 40Gbps at 50m and 100Gbps at 15m.
More things about Category 7
Compared to previous generations of cabling, it is stiffer. In both cases, you can see an extra layer that covers the inner shielded parts. When it comes to cross-talk and system noise, Category 7 becomes unbeatable compared to others. It is compatible with traditional Category 5e and Category6 Ethernet. These cables have Xmultiple’s UltraJAX connectors, which don’t have any contact pins. Although contact pads and a printed circuit board are available in this cable.
A Category7 Cable that we know as a Category 7e cable is used as the cabling infrastructure of Gigabit Ethernet. You can experience frequencies Up to 600MHz. It offers extensive shielding. The category6 also has a few unique GigaGate45 (GG45) connectors. However, if you want the same higher performance features, you must choose the right category wire to support Vat 4t5.
Whether you want to use a cable for home purposes, then you can choose Category7. These are helpful for commercial use also. The Category 7 line is compatible with many devices.
Cat 7a
This Ethernet cable is not available anywhere. It comes with a few supporting networking hardware options. Cat 7a is designed in such a way so that it can support 40 Gigabit Ethernet connections up to 50 meters, similar to the Category7. It has an advanced bandwidth that is more than 50%. But the drawback is that it is more expensive than the other categories.
Cat 8
These CAT 8 cables have a maximum frequency of 2,000MHz. The Category 8 lines offer up to 40Gbps at 30 meters distance. The frequencies of the wires are un-shielded. The cables have two connectors. These connectors keep the cable connected with only three wires at a length of 30 meters. Now a day, these cables are available at reasonable prices. It is the only Ethernet cable type that meets the latest IEEE standards. According to the IEEE standards, these cables have 40Gbps and 2,000MHz frequency network speeds. That’s why; most people prefer to use this cable although it will be costlier than others.
The next generation Cables
Category 9 cable and Category 10 cable are the Ethernet cables that will come after the Category 8 generation.
Shielded (FTP) vs. Unshielded (UTP)
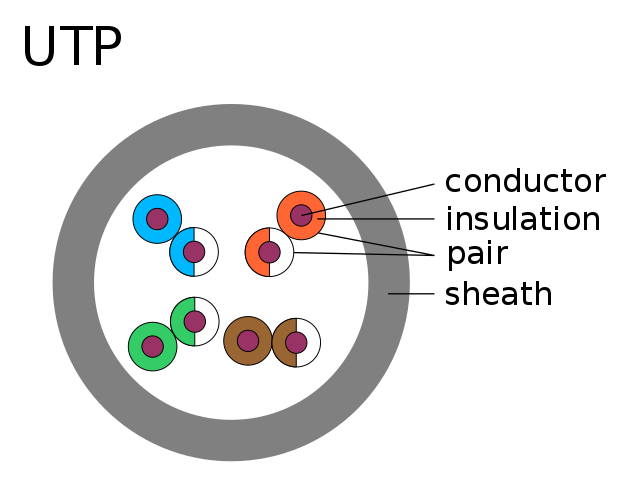
Usually, the twisted pair of copper wires has two different forms: shielded and un-shielded. The difference between these two types is that shielded copper wires contain protective conductive coatings like Copper tape, copper braided strands, or a conductive polymer. This coating helps decrease noise interference. At the same time, the UTP doesn’t have any shielding. You can use it for network areas like typical LAN environments.
TP (Twisted Pairs): These wires indicate those cables that are twisted together. These wires used in industrial cases.
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pairs): You can’t find any shielding in this type of cable. These are flexible and available at cheap rates. The signal quality of these twisted pairs is incredible.
STP or SSTP (Shielded Twisted Pairs): These ethical cables have Braided shielding that helps to keep these protected. These are made from copper and other polymers. The braided shielding is advantageous to decrease noise and improve connection quality.
FTP or SFTP (Foiled Twisted Pairs): The foil shielding protects these twisted wires. These also help to decrease noise and improve connection quality.
Three Ethernet Cabling Alternatives
Powerline Adapters:
The powerline adapters help to transmit data signals with the help of your home’s electrical wiring. The AC power lines have their waveform ( 50-60Hz). But it depends on the location where you live. These alternatives use a wide range of frequencies from 2,000,000 to 86,000,000 Hz. Powerline adapters support all types of wireless electronic devices and share data through WiFi.
PoLRE:
It stands for Power over Long Reach Ethernet. This alternative of Ethernet cable can support IoT devices and IP devices.
Ethernet over COAX (MoCA Adapter):
MoCA stands for Multimedia over COAX. These adapters are quicker than a traditional connection. You can install these cables easily compared to the traditional Ethernet cabling. These alternatives share data signals from a router to devices with the help of the COAX cabling. As a result, you can get network speeds similar to the traditional Ethernet network. These adapters have a maximum network speed of up to 1 Gbit/s.
Ethernet Splitter

While using two spare ports and two devices in different rooms, an Ethernet Splitter can do the best job. It helps you to connect when you keep two devices in one place and a router in another place. And by doing it, you can get a speed of only 100mb/s. These Splitters are very affordable in recent times.
We can see the use of twisted cables in many homes. Category5 cable is a perfect example of it. This cable needs merely four wires to share data signals with devices.
In this case, the number of ports also depends. The more ports the Splitters have, the more speed you can get. When you buy any splitter, you must check whether the Splitter can deliver a superior performance or not.
Advantage:
You can’t use all the eight wires in a 100BASE-T Ethernet cable. But splitters allow you to connect all the cables with devices at a time. You can also use the two remaining ports of that splitter to transmit data signals with devices.
Disadvantages:
- There must be two Ethernet ports in the Splitters
- The Splitters have only 200mb/s limit
- Here, you can only connect two wires at one end
There is a small gizmo in a splitter that contains three Ethernet ports. One port is on one side, and two ports on the other side. Ethernet Splitters are beneficial when you have shortage of cables. One Splitter doesn’t allow you to use many devices that you are using through Ethernet at a time. Here, you need to take the help of another Splitter that can help to un-split the connection back into two wires.
The splitters send data signals from its two physical Ethernet ports to the devices through a single cable. The connection should have maximum 100mbps network speed. You can’t connect both ports of the Splitter together at a time. These ports remain isolated unlike hubs and switches. The Ethernet Splitters never slow down the connection.
If there is any gigabit port in the Ethernet switch, you can get fast internet download speeds. These can be used for 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps UTP Ethernet installations. It doesn’t need power input. But if you want to use Splitters, you must use two wires at a time.
Splitters need to be used in pairs. It physically splits a single Ethernet connection into two connections.
Conclusion:
This article lets you know about the Ethernet cable types and their details. We hope that the details we have given in our article will be beneficial for you.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Why do we use an Ethernet cable?
It is nothing but a typical network cable that can be used at our home or any offices. We also use the Ethernet cables to connect the wired devices to the local network to transmit and access the internet.
Can you use Wi-Fi and Ethernet at the same time?
If you are a PC or Mac user, try to set it up to use the Wi-Fi and Ethernet. But you cannot increase the bandwidth of Wi-Fi and Ethernet networks that you are using to connect with your router. The reason is that both of these transmit a similar upstream network.
Can I connect an Ethernet cable to a TV?
It used to access wireless cable connection. It is a part of the local area network. You can plug the cord of an Ethernet wire into a wireless router for sharing the data to the television. However, the Ethernet cables can’t support all televisions.
Which Ethernet cable is the fastest one?
Category 8 cable is the fastest Ethernet wire. But nowadays, Category 7a cable, known as Cat 7a or Cat 7 “augmented”, offers the highest performance in the market. This cable can also speed up to 10,000 Mbps like Category 7 cable and Category 6 cable. But the maximum bandwidth of this cable is at 1,000 MHz.







