Introduction to Google Search Console
Google Search Console, often abbreviated as GSC, is a robust set of webmaster tools provided by Google. It is an essential platform for website owners, webmasters, and SEO professionals to enhance their website’s performance in Google’s search results. This free tool offers invaluable insights and data about your website’s appearance in Google Search. It also shows how site owner can improve their site for better visibility and user experience.
Google Search Console is a web service offered by Google. It allows you to monitor and manage your website’s performance in Google Search. It provides a wealth of information and tools to help you understand how GoogleBot, Google’s web crawling Bot, interacts with your site. With this data, you can optimize your website to appear more prominently in search results. And you can fix issues that might be hindering your site’s performance. And you can ensure a better user experience for your visitors.
Google Search Console provides:
- Insight into Search Visibility
- Indexing Information
- Website Health
- Structured Data and Rich Results
- Performance Metrics
- Mobile Friendliness
- Integration with Google Analytics
Google Search Console is a vital tool for website owners and SEO practitioners. It offers deep insights into how their websites are performing in Google Search. And it provides what improvements can be made to boost search rankings and user engagement. In the following sections, let us deeply discuss GSC’s various features and tools and how to make the most of this valuable resource.
What is Google Search Console?
Google Search Console is a free web service provided by Google. It allows the user to monitor and manage how websites perform in Google Search. Besides, it offers a range of tools and reports to help users understand how Google’s search engine views their websites. It allows the user to identify issues that might affect search visibility. In addition, the user can optimize their online presence for better search rankings using it.
Primary Functions and Features of Google Search Console
Search Performance Analysis:
GSC provides data on the performance of your website in Google Search. You can see which search queries lead users to your site. You can know how often your pages are displayed in search results. It helps you understand your pages’ average position in search listings. This information is valuable for refining your SEO strategy.
Index Coverage and Sitemap Submission:
The tool offers insights into the indexing status of your website. GSC allows you to identify and address any issues preventing Google from properly indexing your content. You can also submit sitemaps to help Google discover and crawl your pages more effectively.
URL Inspection Tool:
This feature enables you to check the indexing status of individual web pages on your site. You can verify if a specific URL is included in Google’s index and review any potential issues hindering indexing.
Mobile Usability and AMP Reports:
GSC provides reports on your site’s mobile usability. It helps to ensure that your website is mobile-friendly and provides a good user experience on Smartphones and tablets. It also offers insights into Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) for faster loading on mobile devices.
Security and Manual Actions:
You can monitor your website for security issues and manual actions taken by Google. Suppose your site has been penalized or flagged for violations. In this case, GSC provides information on the issues and instructions for resolving them.
Performance Enhancements:
GSC offers data related to page speed and Core Web Vitals. The core web vitals and Page Speed are crucial for user experience and can impact search rankings. It helps you identify and address performance issues to improve your site’s loading times.
Structured Data and Rich Results:
The tool allows you to check if structured data (schema markup) is implemented correctly on your website. Properly structured data can lead to rich search results like featured snippets, recipe cards, and other special search result formats.
International Targeting and Site Settings:
You can set geotargeting preferences. It is to inform Google about your site’s target audience. It also helps you manage domain and URL parameters for better search performance in specific regions or languages.
Integration with Google Analytics:
GSC can be integrated with Google Analytics to combine search performance data with user behavior and conversion data. It provides a comprehensive view of how your website is performing.
Google Search Console is an essential tool for website owners and SEO practitioners to optimize their websites for Google Search. It offers valuable insights, diagnostic tools, and reports. It helps you improve your website’s search rankings, user experience, and overall online visibility.
Why is Google Search Console important for website owners?
Google Search Console is important for website owners for several compelling reasons.
Insight into Search Visibility:
GSC provides website owners with valuable data on how their site is performing in Google Search results. It offers information about which search queries are driving users to your website. Besides, it provides how often your pages are displayed in search results. In addition, it also lets you know the average position of your pages in Google search results. This data helps you understand the keywords and content that are most effective in attracting organic traffic.
Indexing Information:
The tool offers insights into the indexing status of your website. It lets you know which pages are indexed by Google and which may have indexing issues. Suppose Google encounters problems accessing and indexing your content. Hence, GSC will provide detailed reports. It allows you to address issues promptly. And it ensures that your pages are included in search results.
Website Health Monitoring:
Google Search Console is vital for monitoring your website’s overall health. It helps you detect and address security issues like malware or hacking incidents. It also alerts you to manual actions taken by Google, which could result from violations of Google’s webmaster guidelines. Identifying and resolving these issues is crucial to maintaining and improving search rankings.
Structured Data and Rich Results:
GSC allows website owners to check if structured data (schema markup) is correctly implemented. Properly structured data can make your site eligible for rich results, like featured snippets, event cards, or recipe cards, enhancing your visibility in search results.
Performance Metrics:
Google Search Console provides essential performance metrics, like clicks, impressions, and click-through rate (CTR). Additionally, it offers insights into Core Web Vitals. The core web vitals assess the user experience based on page speed and loading performance. This data is critical for improving user experience. And that can positively impact search rankings.
Mobile Friendliness:
As mobile internet usage continues to rise, GSC helps website owners ensure their sites are mobile-friendly and perform well on various devices. It offers mobile usability reports and highlights issues that may affect the mobile user experience.
Integration with Google Analytics:
Google Search Console can be integrated with Google Analytics. That integration allows website owners to correlate search performance data with user behavior and conversion data. In addition, this integration provides a more comprehensive view of how your website is performing. Besides, it shows how search traffic contributes to your website’s goals.
Google Search Console is an indispensable tool for website owners because it empowers them to monitor and improve their search performance. It provides insights into user behavior, indexing, and site health. GSC provides insights into opportunities to enhance visibility in Google Search. By using GSC effectively, website owners can optimize their websites. They can attract more organic traffic and provide a better user experience, ultimately achieving their online goals and objectives.
Getting Started with Google Search Console
Setting up your Google Search Console Account
Google Search Console is a powerful tool for optimizing your website’s performance in Google Search. You must set up your account and add your website to the platform to get started.
How to begin your journey with Google Search Console:
-
Create a Google Account (if you don’t have one)
If you already have a Google Account, you can skip this step. However, you must create a Google Account if you do not have one. This account can access Google Search Console and other Google services.
-
Go to Google Search Console
Visit the Google Search Console website by going to https://search.google.com/search-console.
-
Sign In with Your Google Account
Click on the “Start Now” button. Sign in with the Google Account you want to use for Google Search Console.
-
Add Your Property (Website)
Once you are logged in, you will need to add your website as a “property.” A property in GSC represents your website or web domain.
- Click the “Add Property” button.
- Enter your website’s URL (https://www.yourwebsite.com) in the provided field.
- Click “Continue.”
-
Verify Your Ownership
Before you can access data for your website, Google must verify that you own or have access to the website. There are several verification methods available.
They are:
- HTML file upload: Download the HTML file provided by Google and upload it to your website’s root directory.
- HTML tag: Add an HTML tag to your website’s homepage.
- Domain name provider: Verify using your domain registrar.
- Google Analytics: Suppose your website is already linked to Google Analytics. In that case, you can verify using your GA tracking code.
Choose the method that suits you best. Do not forget to follow the on-screen instructions to complete the verification process.
-
Access Your Search Console Dashboard
Once verification is successful, you will gain access to your Google Search Console dashboard. Here, you will find various sections and reports that provide insights into how your website is performing in Google Search.
-
Submit a Sitemap (Optional)
While not mandatory, submitting a sitemap is highly recommended. A sitemap is an XML file that contains a list of all the pages on your website. It helps Google crawl and index your site more effectively.
To submit a sitemap:
- Click on the “Sitemaps” section in GSC.
- Add the link to your sitemap and click “Submit.”
Congratulations, you have now set up Google Search Console for your website. Now, you can explore the various features and reports to gain insights into your website’s search performance. As you continue to use GSC, you will be able to identify areas for improvement. In addition, you can make data-driven decisions to enhance your website’s presence in Google Search.
Why is Google Search Console important for website owners?
GSC is an indispensable tool for website owners, webmasters, and SEO professionals. It provides more benefits and insights crucial for a website’s success and visibility.
Here is why GSC is of utmost importance:
-
Insight into Search Visibility
GSC offers website owners invaluable data on how their site performs in Google Search. It provides information about which search queries are driving users to your website. And it shows how often your pages are displayed in search results. In addition, it tells you the average position of your pages. This data helps you understand the keywords and content that are most effective in attracting organic traffic.
-
Indexing Information
The tool offers insights into the indexing status of your website. It lets you know which pages are indexed by Google and which may have indexing issues. GSC will provide detailed reports if Google encounters problems accessing and indexing your content. And it allows you to address issues promptly and ensure that your pages are included in search results.
-
Website Health Monitoring
Google Search Console is vital for monitoring your website’s overall health. It helps you detect and address security issues, like malware or hacking incidents. It also alerts you to manual actions taken by Google, which could result from violations of Google’s webmaster guidelines. Identifying and resolving these issues is crucial to maintaining and improving search rankings.
-
Structured Data and Rich Results
GSC allows website owners to check if structured data (schema markup) is correctly implemented. Properly structured data can make your site eligible for rich results, like featured snippets, event cards, or recipe cards. Those can enhance your visibility in search results.
-
Performance Metrics
Google Search Console provides essential performance metrics, like clicks, impressions, and click-through rate (CTR). Additionally, it offers insights into Core Web Vitals. And the insights can assess the user experience based on page speed and loading performance. This data is critical for improving user experience, which can positively impact search rankings.
-
Mobile Friendliness
Mobile internet usage continues to rise. Therefore, GSC helps website owners ensure their mobile-friendly sites perform well on various devices. It offers mobile usability reports and highlights issues that may affect the mobile user experience.
-
Integration with Google Analytics
Google Search Console can be integrated with Google Analytics. That integration allows website owners to correlate search performance data with user behavior and conversion data. This integration provides a more comprehensive view of your website’s performance and how search traffic contributes to your website’s goals.
Google Search Console is an essential tool for website owners because it empowers them to monitor and improve their search performance. It provides insights into user behavior, indexing, and site health. In addition, it offers opportunities to enhance visibility in Google Search. By using GSC effectively, website owners can optimize their websites. They can attract more organic traffic to provide a better user experience. They can ultimately achieve their online goals and objectives. It is a powerful ally in the ever-competitive online landscape. Further, it helps website owners make data-driven SEO and user engagement decisions.
Verifying your website
Verifying your website in Google Search Console is critical in establishing your ownership or access rights. And that process grants you access to valuable search-related data and tools. Verification ensures only authorized users can manage website data in the Google Search Console.
Below are the steps to verify your website:
-
Access Your Google Search Console Property
- Log in to your Google Search Console account.
- On the home page, select the property (website) you want to verify if you have multiple properties.
-
Choose a Verification Method
Google Search Console offers various methods to verify your website. Select the method that is most convenient for you and your technical expertise. Common verification methods include:
- HTML File Upload: This method involves downloading an HTML verification file provided by Google. You need to upload it to your website’s root directory using your hosting provider’s FTP client or file manager.
- HTML Tag: You can add an HTML tag to your website’s homepage by copying the provided Meta tag and pasting it into the HTML code of your site’s homepage. Ensure the tag is placed within your HTML’s <head> section.
- Domain Name Provider (DNS Verification): This method involves changing your domain’s DNS records. It is typically done by adding a DNS TXT record or CNAME record provided by Google. This method may require more technical knowledge and control over your domain’s DNS settings.
- Google Analytics: Suppose your website is already linked to Google Analytics. In that case, you can verify your website ownership through your Google Analytics account. This is often the simplest method if you are already using Google Analytics.
-
Complete the Verification Process
Depending on your chosen method, follow the specific instructions provided by Google. Here are some general guidelines:
- HTML File Upload: Download the verification HTML file. And upload it to your website’s root directory. Then click the “Verify” button in Google Search Console. Google will check for the existence of the file on your server.
- HTML Tag: Copy the HTML tag provided by Google and paste it into your website’s HTML code within the <head> section. After making the change, return to Google Search Console and click the “Verify” button.
- Domain Name Provider (DNS Verification): Access your domain registrar or DNS provider, add the DNS record as instructed by Google, and wait for the DNS changes to propagate. This process may take some time.
- Google Analytics: Select the Google Analytics verification method. And Google will check your Google Analytics account for ownership verification. Ensure that the Google Analytics property is correctly linked to your website.
-
Verify Your Ownership
After following the verification steps and clicking the “Verify” button in the Google Search Console, Google will check whether the verification method was successful. If successful, you will receive a confirmation message, and your website will be verified.
Congratulations! You have successfully verified your website in the Google Search Console. Successful verification grants you access to important data, reports, and tools to monitor and enhance your website’s performance in Google Search. Remember that you may need to re-verify your website if you significantly change your domain or hosting setup.
Navigating the Google Search Console Dashboard
Navigating the GSC dashboard is essential to effectively use the tool and gain insights into your website’s performance in Google Search. The GSC dashboard provides an overview of various reports and features.
Here is a guide on how to navigate the GSC dashboard:
-
Access Your Property:
Log in to your Google Search Console account and select the property (website) you want to analyze. Choose the one you want to work with if you have multiple properties.
-
Dashboard Overview:
The GSC dashboard provides a snapshot of key performance metrics and reports. All are accessible from the left-hand sidebar. Here are the key sections and how to navigate them:
-
Performance:
Click “Performance” in the sidebar to access the performance data. This section provides a summary of how your site is performing in Google Search. You can view clicks, impressions, click-through rate (CTR), and average position data. Filter data by date range, queries, pages, countries, and devices.
-
Coverage:
The “Coverage” section allows you to see how many of your pages are indexed and whether any errors or issues prevent indexing. This information helps you identify and fix problems with your website’s pages.
-
Sitemaps:
In this section, you can view and submit sitemaps for your website. Sitemaps help Google crawl and index your pages efficiently.
-
URL Inspection:
Use the “URL Inspection” tool to check the indexing status and coverage of specific pages on your website. Enter the URL you want to inspect and receive details about its status.
-
Mobile Usability:
The “Mobile Usability” section provides insights into how well your site performs on mobile devices. It highlights issues that could impact the mobile user experience.
-
AMP:
If you have implemented Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) on your site, you can find reports on AMP issues and performance in this section.
-
Security & Manual Actions:
This section informs you about potential security issues on your site and any manual actions Google takes. It is crucial for maintaining a safe and trusted website.
-
Enhancements:
The “Enhancements” section helps you monitor structured data on your site. You can track how Google understands and presents your content in search results.
-
International Targeting:
This section allows you to set Geotargeting This section manages how your website is displayed in specific countries or languages.
-
Core Web Vitals:
GSC provides insights into Core Web Vitals. Those measure your website’s user experience and loading performance. It is essential for maintaining a user-friendly site.
-
-
Data and Reports:
In each section of the GSC dashboard, you can access detailed data, reports, and diagnostic tools by clicking on specific items or links. Explore the reports to identify issues, track improvements, and analyze your site’s performance.
-
Search Appearance:
While not listed in the sidebar, you can navigate “Search Appearance” to see how your site appears in search results. This includes structured data, rich results, and more.
-
Search Traffic:
Although not part of the primary dashboard, the “Search Traffic” section in the sidebar contains additional reports on search queries, links to your site, and internal links.
-
Manual Actions:
Suppose your website has received manual actions from Google. In that case, you can review and address them under the “Security & Manual Actions” section.
By navigating through these sections and reports within the Google Search Console dashboard, you can gain valuable insights into your website’s performance in Google Search. You can identify areas for improvement. Besides, you can make data-driven decisions to enhance your website’s visibility and user experience. Regularly monitor your GSC dashboard to track changes and maintain a healthy and well-optimized website.
Overview of the dashboard
GSC dashboard provides website owners with a centralized hub to monitor and optimize their website’s performance in Google Search.
Property Selector:
At the top left corner, you will find a dropdown menu that allows you to select the specific property (website) you want to analyze. It is helpful if you have multiple properties associated with your Google Search Console account. Choose the property you want to work with.
Performance:
The “Performance” section provides a snapshot of how your website is performing in Google Search. It displays key metrics like total clicks, total impressions, average click-through rate (CTR), and average position. You can customize the date range for your data. You can apply filters and drill down into specific reports to analyze search performance further.
URL Inspection:
The “URL Inspection” tool allows you to check the indexing status and coverage of specific URLs on your website. You can enter a URL to inspect and receive detailed information about its status, indexing, and any issues Google may have encountered.
Index Coverage:
The “Coverage” section gives you insights into how many of your website pages are indexed by Google. And you can know if there are any errors or issues preventing indexing. It provides a summary of your site’s index coverage. And it highlights pages with problems.
Sitemaps:
In the “Sitemaps” section, you can view the status of submitted sitemaps and submit new sitemaps. Sitemaps help Google crawl and index your website’s content more efficiently.
Mobile Usability:
The “Mobile Usability” report shows whether your website is mobile-friendly. And mobile usability provides insights into potential mobile usability issues. Ensuring a positive mobile experience is crucial due to the increasing number of mobile users.
AMP:
Suppose you have implemented Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) on your site. In that case, this section offers insights into your AMP pages’ performance and issues. AMP pages are designed for faster mobile loading.
Security & Manual Actions:
This section provides information about potential security issues detected on your website and any manual actions Google takes. You can review and address security issues to maintain a trustworthy website.
Enhancements:
The “Enhancements” section helps you monitor your site’s structured data (schema markup). It provides insights into how Google understands your content and any enhancements you can implement to improve search results.
International Targeting:
In this section, you can set Geotargeting preferences and manage your website’s appearance in search results in specific countries or languages. This is particularly useful if you have a global audience.
Core Web Vitals:
GSC offers insights into Core Web Vitals. It measures your website’s user experience and loading performance. It is essential for providing a smooth and fast browsing experience to visitors.
Additional Reports:
The “Search Appearance” section lets you see your site’s appearance in search results. That includes structured data, rich results, and more. Additionally, the “Search Traffic” section provides reports on search queries, links to your site, and internal links.
Overall, the GSC dashboard is designed to provide website owners with a comprehensive view of their website’s performance in Google Search. It is a valuable tool to monitor. It helps you to diagnose issues. And you can make data-driven decisions to improve search rankings, user experience, and overall website visibility. Regularly checking and analyzing data within the dashboard can help you maintain and enhance your website’s presence in Google Search.
Key data and metrics displayed
In GSC, various key data and metrics are displayed in different sections of the dashboard and reports. These data and metrics provide valuable insights into how your website is performing in Google Search.
Here are some of the essential data and metrics you can expect to find:
-
Performance Metrics:
- Total Clicks: The total number of clicks that users made on your website’s search results in Google.
- Total Impressions: The total number of times your website’s pages were displayed in Google’s search results.
- Average Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of clicks compared to impressions. That indicates the effectiveness of your search results in attracting clicks.
- Average Position: The average ranking position of your website’s pages in Google’s search results.
-
Index Coverage:
- Valid Pages: The number of indexed pages and error-free pages.
- Excluded Pages: The number of pages that Google has chosen not to index due to errors or other issues.
- Coverage Errors: Detailed information about the indexing issues your website may encounter.
-
URL Inspection:
- Indexing Status: Whether a specific URL is included in Google’s index.
- Crawling Information: Details about when Google last crawled and indexed the URL.
- Mobile Usability: Information on mobile usability for the URL.
-
Sitemaps:
- Submitted Sitemaps: A list of the sitemaps you have submitted.
- Indexed Pages: The number of pages that are indexed as a result of the submitted sitemaps.
-
Mobile Usability:
- Mobile Usability Issues: Specific mobile usability problems that Google has detected on your website.
-
AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages):
- AMP Page Validity: Information on the validity of AMP pages on your site.
- AMP Page Errors: Detailed information on AMP page errors, if any.
-
Security & Manual Actions:
- Security Issues: Details about any security issues Google has found on your website.
- Manual Actions: Notifications of manual actions taken by Google. That includes any penalties or actions against your site.
-
Enhancements:
- Structured Data: Information about implementing and validating structured data (schema markup) on your site.
- Rich Results: Insights into how your site’s pages appear in rich results or special search result formats.
-
International Targeting:
- Country or Language Targeting: Information on how your website is targeted for specific countries or languages.
-
Core Web Vitals:
- Page Loading Metrics: Insights into Core Web Vitals metrics, including Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
These are just some of the key data and metrics in Google Search Console. The availability of specific metrics and reports may vary depending on the section and the features you have implemented on your website. Monitoring and analyzing this data is crucial for understanding your website’s performance. It helps you to identify issues and make improvements to enhance your website’s visibility in Google Search.
Search Performance Analysis
Search performance analysis in Google Search Console is a critical process that involves examining the data and metrics related to how your website is performing in Google Search. This analysis helps you understand user behavior. Users can identify strengths and weaknesses. And you can make informed decisions to improve your website’s search visibility.
How to Conduct a Search Performance Analysis:
-
Access the Performance Report:
- Log in to your Google Search Console account.
- Select the property (website) you want to analyze.
- Click on the “Performance” section in the left sidebar.
-
Choose a Date Range:
- By default, the performance report displays data for the last three months. You can adjust the date range to analyze data for specific periods. This is useful for tracking changes over time, like the impact of SEO improvements or algorithm updates.
-
Review Key Metrics:
- Total Clicks: The total number of clicks users made on your website’s search results.
- Total Impressions: The total number of times your website’s pages were displayed in Google’s search results.
- Average Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of clicks compared to impressions, indicating how well your search results attract clicks.
- Average Position: The average ranking position of your website’s pages in Google’s search results.
-
Filter and Compare Data:
- Use filters to narrow down the data you want to analyze. For prodigitalweb, you can filter by specific queries, pages, countries, devices, or search appearance features.
- Compare different metrics to identify trends. For instance, comparing CTR and position can help you understand if higher rankings lead to more clicks.
-
Identify Top Queries and Pages:
- Examine the queries that are driving the most traffic to your website. Are there specific keywords that perform well?
- Review the top-performing pages on your site. Are there specific pages that consistently receive high clicks and impressions?
-
Analyze Click-Through Rate (CTR):
- Look for pages with a high number of impressions but a low CTR. This indicates that users are seeing your pages but not clicking through. These pages may need better titles or Meta descriptions to entice clicks.
-
Examine Average Position:
- Identify pages close to reaching the first page of search results (positions 1-10). Improving the ranking of these pages can significantly boost their visibility.
-
Review Click Trends:
- Are clicks, impressions, or CTR fluctuations corresponding to specific events or updates? Identify what caused these changes and learn from them.
-
Spot Seasonal Trends:
- If your website experiences seasonal fluctuations, look for patterns in search performance. Adjust your strategies accordingly.
-
Set Goals and Take Action:
- Based on your analysis, set specific goals to improve search performance. This may involve optimizing content, fixing technical issues, or focusing on specific keywords.
- Track the impact of your actions by regularly revisiting the performance report. Adjust your strategies based on the results.
- Monitor Performance Over Time:
- Regularly monitor and compare performance data to track improvements or potential issues. Stay informed about changes in user behavior and search trends.
Search performance analysis is an ongoing process essential for optimizing your website’s visibility and attracting organic traffic. By consistently reviewing and acting upon the insights provided by Google Search Console, you can enhance your website’s performance in Google Search and meet your SEO goals.
Understanding Search Queries and Keywords
Understanding search queries and keywords is fundamental for successful search engine optimization and improving your website’s performance in search engine results. Let us break down these concepts:
-
Search Queries:
- What are Search Queries? Search queries are often referred to as search terms or search strings. Users enter these phrases or words into a search engine like Google when looking for information, products, services, or answers to their questions.
- User Intent: Search queries reflect the intent of the user. It is essential to understand why someone is searching, what they hope to find, and what actions they might take after finding the information they seek.
- Types of Search Queries:
- Informational Queries: Users seek information or answers to questions (“How to tie a tie”).
- Navigational Queries: Users are looking for a specific website or page (“Facebook login”).
- Transactional Queries: Users intend to perform a specific action or make a purchase (“Buy iPhone 13”).
- Commercial Queries: Users are researching products or services with the intention of buying (“Best digital cameras 2023”).
-
Keywords:
- What are Keywords? Keywords are specific words or phrases you target in your content and SEO efforts to match the search queries users enter into search engines. Keywords help search engines understand the relevance of your content to specific queries.
- Keyword Research: Conducting keyword research identifies the most relevant and effective keywords for your website or content. This involves finding keywords with a balance between search volume and competition.
- Long-Tail Keywords: Long-tail keywords are longer and more specific keyword phrases. They often have a lower search volume but can be highly valuable for niche topics. (“Best budget gaming laptop under $500”).
- Keyword Optimization: Once you have selected relevant keywords, you optimize your content by incorporating these keywords naturally into your text, headings, Meta tags, and URLs.
-
Understanding the Relationship:
- To optimize your website for search engines, you need to align your content with users’ search queries. This involves:
- Creating High-Quality Content: Developing content that answers common search queries with valuable information, relevance, and quality.
- On-Page SEO: Optimize your web pages by using relevant keywords in title tags, meta descriptions, headings, and content.
- User Intent Alignment: Ensuring your content matches the intent behind specific search queries. Different pages may target informational, navigational, or transactional queries.
- Tools like Google Search Console and keyword research tools can help you identify the search queries that bring users to your site. Use this data to refine your keyword strategy and improve your content.
- To optimize your website for search engines, you need to align your content with users’ search queries. This involves:
Remember that the SEO landscape is constantly evolving, and understanding user intent, optimizing for voice search, and providing valuable, relevant content are becoming increasingly important. Regularly reviewing your website’s performance in Google Search Console will help refine your keyword strategy effectively. In addition, it can align your content with user needs.
Analyzing Clicks, Impressions, and Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Analyzing clicks, impressions, and click-through rate (CTR) is crucial to understanding and improving your website’s performance in search engine results. These metrics provide insights into how users interact with your site’s search results. And it can guide your SEO efforts.
How to analyze them effectively:
-
Clicks:
- Definition: Clicks represent the number of times users clicked on your website’s search result and visited your site from the search engine results page (SERP).
- Analysis:
- Many clicks indicate that your search results are appealing and relevant to users.
- Low click counts may suggest that your search result titles or descriptions need improvement or that users are not finding what they’re looking for on your pages.
- Action Steps:
- Analyze which pages receive the most clicks and determine why they are successful. Optimize other pages to emulate their success.
- Review your Meta titles and descriptions to ensure they are compelling and accurately describe your content.
-
Impressions:
- Definition: Impressions represent the number of times your website’s pages appear in search results, whether or not users click on them. An impression occurs each time your page is viewed on the SERP.
- Analysis:
- High impression counts show that your pages are frequently displayed in search results.
- Low impressions may suggest your pages are not ranking well for relevant queries.
- Action Steps:
- Investigate which queries and pages generate the most impressions. Optimize these pages to increase their click-through rate.
- Focus on improving your website’s SEO to enhance rankings and increase visibility in search results.
-
Click-Through Rate (CTR):
- Definition: CTR is the ratio of clicks to impressions. It is expressed as a percentage. It indicates how often users click on your search result when they see it in the SERP.
- Analysis:
- A high CTR indicates that your search result is highly appealing to users.
- A low CTR suggests your search result may not meet user expectations or be compelling enough.
- Action Steps:
- Review your search result titles and Meta descriptions to make them more engaging and relevant to your target queries.
- Compare CTR for different queries and pages to identify trends and opportunities for improvement.
-
Segmentation and Filters:
- In Google Search Console or other analytics tools, you can segment and filter data by various criteria like specific queries, pages, countries, devices, and date ranges. This allows you to focus on specific aspects of your data for in-depth analysis.
-
Monitoring Trends:
- Monitor clicks, impressions, and CTR data over time to identify trends. For prodigitalweb, you may notice seasonal fluctuations or changes in user behavior that require adjustments to your SEO strategy.
-
A/B Testing:
- Experiment with variations of your Meta titles and descriptions to see how they affect CTR. A/B testing can help you determine which copy is most effective.
-
Competitor Analysis:
- Compare your CTR with that of competitors for the same queries. This can provide insights into how you stack up against others in the search results.
By analyzing clicks, impressions, and CTR, you can better understand how your website performs in search results and make informed decisions to improve your SEO strategy. Consistently optimizing your search result listings and aligning them with user intent is primary to increasing clicks and overall search visibility.
Index Coverage and Sitemap Submission
Index coverage and sitemap submission are important aspects of managing your website’s presence in search engines like Google. These processes help ensure your site is properly crawled, indexed, and displayed in search results.
Here is an overview of both:
Index Coverage:
Index coverage refers to how well search engines index your website’s pages. The goal is to have all your important pages indexed with minimal errors. Google Search Console provides insights into your site’s index coverage.
- Access the Coverage Report:
- Log in to Google Search Console.
- Select your property (website).
- Click on “Index” in the left sidebar. And then choose “Coverage.”
- Review the Coverage Report:
- The report provides information about indexed pages, valid pages, errors, and pages excluded from indexing.
- Pay attention to the “Errors” section. The error section highlights issues that may prevent proper indexing. These errors could include broken links, server errors, or page content problems.
- Address Indexing Issues:
- Review the error details and take action to fix issues. This might involve updating content, fixing broken links, or addressing server errors.
- Recheck the coverage report regularly to confirm that issues are resolved.
- Request Indexing:
- If you have made significant changes to your site, you can request indexing in Google Search Console. This can help ensure that your updated content is reflected in search results.
Sitemap Submission:
A sitemap is a structured file that provides search engines with information about your website’s pages. Submitting a sitemap can help search engines discover and index your pages more efficiently.
- Generate a Sitemap:
- Use a sitemap generator tool or a content management system (CMS) Plugin to create an XML sitemap. It should list all your website’s pages.
- Submit the Sitemap:
- Access Google Search Console.
- Select your property.
- Click on “Sitemaps” in the left sidebar.
- Enter the URL of your sitemap (https://www.prodigitalweb.com/sitemap.xml) and click “Submit.”
- Monitor Sitemap Status:
- After submission, you can monitor the status of your sitemap. Google Search Console will provide information about the number of submitted pages and the number of indexed pages.
- Regularly Update Your Sitemap:
- As you add or remove pages on your website, ensure that your sitemap is updated to reflect these changes.
You need to address index coverage issues and submit a sitemap. So that you improve your website’s chances of being fully indexed and displayed in search results. Regularly monitoring your coverage report and sitemap status is essential for maintaining a healthy and well-optimized website in the eyes of search engines.
Monitoring the Index Status of Your Webpages
Monitoring the index status of your webpages is crucial to ensure that search engines correctly index your site’s pages. By regularly checking and optimizing your index status, you can maintain your website’s visibility in search results.
Here is how to monitor the index status of your webpages:
-
Google Search Console:
- Access Google Search Console: Log in to your Google Search Console account.
- Select Your Property: Choose the property (website) you want to monitor. If you have not added your site to the Google Search Console, you must do that first.
- Index Coverage Report: In the left sidebar, click “Index” and select “Coverage.”
- Review the Coverage Report: This report provides detailed information about the index status of your Webpages. Here are some key elements to pay attention to:
- Valid Pages: These are pages that Google has successfully indexed. Ensure that all your important pages fall into this category.
- Errors: Check for any errors preventing certain pages from being indexed. Common errors include server errors, crawling issues, and pages blocked by robots.txt.
- Excluded Pages: Excluded pages are those that Google has chosen not to index. Understand the reasons for exclusion, like “noindex” tags or canonical tags.
- Coverage Issues: Investigate issues in the “Coverage Details” section. That provides specific information about pages with errors, warnings, or valid pages. Take action to address these issues.
- Fix Errors: If you identify errors in the report, take steps to resolve them. This may involve fixing broken links, updating content, or addressing server issues.
- Request Indexing: Suppose you have made significant changes to a page or want to expedite the indexing of new content. In that case, you can use the “Request Indexing” feature in Google Search Console.
-
Sitemap and Robots.txt File:
- Check Your Sitemap: Ensure that your XML sitemap lists all the important pages on your website. Make sure it is up to date with your site’s current structure.
- txt File: Review your robots.txt file to ensure you are not accidentally blocking search engine crawlers from accessing important pages.
-
Regular Monitoring:
- Regularly check the index coverage report in Google Search Console to monitor changes and resolve issues promptly.
- Set up email notifications within Google Search Console to receive alerts when detecting indexing issues.
-
Google Analytics:
- Google Analytics focuses more on user behavior and traffic. Besides, it can provide additional insights into how your pages perform regarding user engagement and conversions.
-
Third-Party SEO Tools:
- Consider using third-party SEO tools that provide more advanced monitoring and analysis of index status. These tools can complement the information provided by Google Search Console.
Continuously monitor the index status of your web pages and take action to address any issues. You can ensure that your website is well-optimized for search engines. It, in turn, helps maintain and improve your site’s visibility and rankings in search results. Regularly updated and properly indexed pages are more likely to attract organic traffic and achieve your SEO goals.
How to submit and manage sitemaps
Submitting and managing sitemaps is essential to ensuring that search engines discover, crawl, and index your website’s pages.
Here is how to submit and manage sitemaps effectively:
-
Generate Your Sitemap:
Before you can submit a sitemap, you need to create one. A sitemap is an XML file that lists all the pages on your website. It provides important information to search engines. There are several ways to generate a sitemap:
- Use a Content Management System (CMS): Many CMS platforms, like WordPress, have plugins or built-in functionality to generate sitemaps automatically.
- Use Sitemap Generator Tools: Various online tools and software applications can create sitemaps for your website. Some popular options include Screaming Frog, Yoast SEO (for WordPress), and XML-sitemaps.com.
-
Verify Ownership in Google Search Console:
Before you can submit a sitemap to Google, you need to verify ownership of your website in Google Search Console. Here is how to do it:
- Sign in to Google Search Console (formerly Google Webmaster Tools).
- Add your website property by following the provided instructions. You can use different verification methods, like adding an HTML tag to your site or verifying through your Google Analytics account.
-
Submit Your Sitemap:
Once you have verified ownership, you can submit your sitemap to Google Search Console:
- In Google Search Console, select the property for your website.
- In the left sidebar, click on “Sitemaps.”
- Click the “Add/Test Sitemap” button.
- Enter the path to your sitemap file. For prodigitalweb, if your sitemap is located at “https://www.prodigitalweb.com/sitemap.xml,” you would enter “/sitemap.xml.”
- Click “Submit.”
-
Monitor Sitemap Status:
After submitting your sitemap, you can monitor its status in Google Search Console:
- Go to the “Sitemaps” section in Google Search Console.
- You will see a list of submitted sitemaps and their status. Check for any issues or errors.
-
Update Your Sitemap:
- Regularly update your sitemap to include new pages, remove deleted pages, and make any necessary changes to the URLs listed.
- Resubmit the updated sitemap in Google Search Console.
-
Monitor Indexing and Performance:
- Continuously monitor your website’s index coverage and performance in Google Search Console. Monitor which pages are indexed and how they perform in search results.
- Use the coverage report in Google Search Console to identify any issues affecting your pages’ indexing.
-
Submit to Other Search Engines:
- Suppose you want your site to be indexed by other search engines, like Bing, Yandex, or Baidu. Hence, check if they offer webmaster tools or search console platforms. Similar to Google Search Console, you can submit your sitemap to these services.
Submit and manage your sitemap effectively. You help search engines discover and index your website’s pages by submitting. That can improve your site’s visibility in search results. Regularly monitoring your sitemap and website’s performance in search results is essential for maintaining and enhancing your SEO efforts.
URL Inspection Tool
The URL Inspection Tool is a feature within Google Search Console (Google Webmaster Tools). It allows website owners and webmasters to check the status of specific URLs on their websites. This tool provides detailed information about how Googlebot, Google’s web crawler, sees and processes individual URLs. That is helping you understand how your web pages are indexed. It also helps to discover any issues that may affect their performance in search results.
How to Use the URL Inspection Tool:
-
Access Google Search Console:
- Log in to your Google Search Console account. If you have not added your website property, you will need to do so to use the tool.
-
Enter the URL for Inspection:
- In the left sidebar, click on “URL Inspection.”
- In the URL Inspection Tool, enter the URL you want to inspect and press the “Enter” key or click the “Inspect” button.
-
Review the Inspection Results:
- The tool will provide information about the URL’s indexing status and other details:
- Indexing Status: You will see whether the URL is indexed or not. Google may provide information about when it was last crawled and indexed.
- Crawl Information: Details about the last time Googlebot visited the URL and if it encountered any issues while crawling.
- Mobile Usability: Information on how mobile-friendly the page is and whether mobile usability issues exist.
- Index Coverage: Data on whether the page is eligible for indexing and if It is blocked by robots.txt or contains a “noindex” tag.
-
Request Indexing:
- If the URL is not indexed, and you believe it should be, you can request indexing by clicking the “Request Indexing” button. Google will then crawl and reevaluate the page for indexing.
-
Troubleshoot Issues:
- If the URL has issues like being blocked by robots.txt, containing a “noindex” tag, or having mobile usability problems, the URL Inspection Tool will highlight these issues.
- Address any identified issues and resubmit the URL for inspection after making necessary changes.
-
Explore Additional Information:
- You can also access more details about the URL, including rendering information and any structured data detected on the page. This additional information can help you understand how Googlebot interprets your page’s content.
-
Monitor Changes:
- You can return to the URL Inspection Tool regularly to check the status of specific URLs and monitor any changes in indexing, crawl frequency, or issues.
The URL Inspection Tool is valuable for diagnosing and resolving issues related to individual pages on your website. It is particularly helpful when you have updated your pages or want to ensure that Google correctly indexes specific content. Regularly using this tool can help improve your website’s performance in search results and maintain a healthy, well-optimized site.
How to use the URL Inspection tool
The URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console is a powerful tool. It allows you to check the status of individual URLs on your website and gain insights into how Googlebot sees and processes those URLs.
Here is how to use the URL Inspection Tool effectively:
-
Access Google Search Console:
- Log in to your Google Search Console account. If you have not added your website property, you need to do so to use the tool.
-
Navigate to the URL Inspection Tool:
- In the left sidebar, click on “URL Inspection.”
-
Enter the URL You Want to Inspect:
- In the URL Inspection Tool, you will find a search bar. Enter the URL of the specific page you want to inspect, press the “Enter” key, or click the “Inspect” button.
-
Review the Inspection Results:
- The tool will provide detailed information about the URL you have inspected, including:
- Indexing Status: The tool will show whether the URL is indexed or not and, if so when it was last crawled and indexed.
- Crawl Information: Details about the last time Googlebot visited the URL and if any issues were encountered during the crawl process.
- Mobile Usability: Information on how mobile-friendly the page is and whether mobile usability issues exist.
- Index Coverage: Data on whether the page is eligible for indexing, whether it is blocked by robots.txt, or if it contains a “noindex” tag.
-
Request Indexing:
- Suppose the URL is not indexed, and you believe it should be. Then, you can request indexing by clicking on the “Request Indexing” button. Google will then crawl and reevaluate the page for indexing.
-
Troubleshoot Issues:
- If the URL has issues like being blocked by robots.txt, containing a “noindex” tag, or having mobile usability problems, the URL Inspection Tool will highlight these issues. Click on the specific issue to learn more.
- Address any identified issues and make the necessary changes to improve the URL’s indexing and performance.
-
Explore Additional Information:
- You can click on the tabs for “Coverage,” “Enhancements,” and “Coverage Issues” to access more details about the URL. Those details include rendering information and any structured data detected on the page.
-
Monitor Changes:
- You can return to the URL Inspection Tool regularly to check the status of specific URLs and monitor any changes in indexing, crawl frequency, or issues.
-
Use for Debugging and Optimization:
- Use the tool to diagnose issues with individual pages and ensure they are optimized for search engines. It is particularly useful when you have made updates to specific pages or want to understand why a page is not being indexed as expected.
The URL Inspection Tool is a valuable resource for website owners and webmasters. It allows them to pinpoint and address issues on a page-by-page basis. In addition, it helps maintain a healthy and well-optimized website. It ensures that individual pages are correctly indexed and perform well in search results.
Checking Indexing Status for Specific Pages
You can use the Google Search Console’s URL Inspection Tool to check the indexing status for specific pages on your website.
How to do it:
-
Access Google Search Console:
- Log in to your Google Search Console account.
-
Navigate to the URL Inspection Tool:
- In the left sidebar, click on “URL Inspection.”
-
Enter the URL to Inspect:
- In the URL Inspection Tool, you will see a search bar. Enter the specific URL of the page for which you want to check the indexing status. You can simply paste the URL, press the “Enter” key, or click the “Inspect” button.
-
Review the Inspection Results:
- The tool will provide detailed information about the URL you have inspected, including:
- Indexing Status: You will see whether the URL is indexed or not and the date of the last crawl and index.
- Crawl Information: Details about the most recent crawl and any issues encountered during crawling.
- Mobile Usability: Information on mobile-friendliness and mobile usability issues.
- Index Coverage: Data on whether the page is eligible for indexing, whether it is blocked by robots.txt, or if it contains a “noindex” tag.
- The tool will provide detailed information about the URL you have inspected, including:
-
Request Indexing (if needed):
- If the URL is not indexed, and you believe it should be, you can use the “Request Indexing” button to request Google to crawl and reevaluate the page for indexing.
-
Troubleshoot Issues:
- If the URL has issues preventing proper indexing like being blocked by robots.txt or containing a “noindex” tag, the URL Inspection Tool will highlight these issues. You can click on the specific issue for more details.
-
Address any identified issues and make the necessary changes to improve the URL’s indexing and performance.
-
Explore Additional Information:
- You can click on the tabs for “Coverage,” “Enhancements,” and “Coverage Issues” to access more details about the URL, including rendering information and any structured data detected on the page.
-
Monitor Changes:
- You can use the URL Inspection Tool regularly to check the status of specific URLs and monitor any changes in indexing, crawl frequency, or issues.
This tool is particularly useful for debugging and optimizing specific pages on your website. It allows you to understand why a particular page may not be indexed as expected and provides valuable insights to help you maintain and enhance your website’s visibility in search results.
Mobile Usability and AMP Reports
Mobile usability and Accelerated Mobile Pages reports are features within Google Search Console that help website owners ensure their websites are mobile-friendly and optimized for a better user experience on mobile devices.
Here is an overview of both reports:
Mobile Usability Report:
The Mobile Usability Report in Google Search Console provides insights into how well your website performs on mobile devices and identifies any issues that may affect the mobile user experience.
- Access the Mobile Usability Report:
- Log in to your Google Search Console account.
- Select your website property.
- In the left sidebar, click “Enhancements” and choose “Mobile Usability.”
- Review Mobile Usability Issues:
- The report will display any mobile usability issues found on your site, like text that’s too small to read, clickable elements that are too close together and mobile viewport issues.
- Address Mobile Usability Issues:
- Click on each issue to get more details and suggestions on how to fix the problem.
- Resolve the issues to ensure a better mobile user experience. That can improve your website’s rankings in mobile search results.
AMP Report (Accelerated Mobile Pages):
The AMP Report in Google Search Console focuses on Accelerated Mobile Pages. The AMP pages are designed to provide faster loading and more efficient mobile content.
- Access the AMP Report:
- Log in to your Google Search Console account.
- Select your website property.
- In the left sidebar, click “Enhancements” and choose “AMP.”
- Review AMP Issues:
- The report will show any AMP issues detected on your site, like validation errors or pages not indexed as AMP.
- Address AMP Issues:
- Click on each issue for more details and guidance on fixing it.
- Correct the issues to ensure that your AMP pages are properly validated and indexed, which can lead to improved mobile performance.
- Monitor AMP Page Performance:
- Regularly check the AMP Report to monitor the performance and status of your AMP pages. This can help you maintain a high-quality user experience for mobile users.
Both the Mobile Usability Report and AMP Report are essential for providing a seamless and efficient mobile experience to your website’s visitors. Address mobile usability issues and ensure your AMP pages are validated and indexed. That can positively impact your site’s rankings in mobile search results. Besides, it increases user engagement and improves overall mobile performance. Regularly monitoring these reports and taking action to resolve issues is crucial for maintaining a mobile-friendly website.
Ensuring Your Site is Mobile-Friendly
Ensuring that your website is mobile-friendly is essential. That is given the significant portion of internet users accessing mobile websites. A mobile-friendly website provides a better user experience and helps with search engine rankings.
How to Make Your Site Mobile-Friendly:
-
Responsive Web Design:
- Use a responsive web design approach. It means your website adapts its layout and content to fit the screen size of the user’s device. This ensures your site looks and functions well on various screen sizes, from Smartphones to tablets and desktops.
-
Mobile-Friendly Templates and Themes:
- Suppose you are using a content management system (CMS) like WordPress. Then, you need to choose templates or themes that are designed to be mobile-friendly or responsive. Many CMSs offer mobile-responsive themes out of the box.
-
Test Your Website:
- Use mobile testing tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to check if your website is mobile-friendly. This tool will provide suggestions for improvements.
-
Optimize Page Load Speed:
- Ensure that your web pages load quickly on mobile devices. Compress images, use browser caching, and minimize the use of large files, scripts, and unnecessary code. Faster load times are essential for a positive mobile user experience.
-
Mobile Navigation:
- Make sure your website’s navigation is user-friendly on mobile devices. Use a simple and intuitive menu system that is easy to access and navigate with a touch screen.
-
Use Mobile-Friendly Fonts:
- Choose readable fonts and font sizes that work well on small screens. Avoid using very small or complex fonts that may be difficult to read on mobile devices.
-
Touch-Friendly Elements:
- Ensure all clickable elements, like buttons and links, are appropriately sized and spaced to accommodate touchscreen interactions. Users should be able to tap on elements without difficulty.
-
Avoid Pop-Ups:
- Pop-ups can be especially annoying on mobile devices. If you use pop-ups for advertisements or lead generation, consider using less intrusive alternatives or ensure they are easy to close on mobile.
-
Mobile SEO:
- Optimize your website for mobile search engines. This includes creating mobile sitemaps and using structured data to help search engines understand your mobile content.
-
Testing on Real Devices:
- Test your website on a variety of real mobile devices and browsers. This can help you identify specific issues that automated testing may miss.
-
Mobile-First Indexing:
- Google uses mobile-first indexing. That means it primarily uses the mobile version of your site to determine search engine rankings. Ensure your mobile site has the same content and metadata as the desktop version.
-
Content Optimization:
- Tailor your content for mobile users. Use shorter paragraphs, bullet points, and concise headings to make consuming on a small screen easier.
-
User Testing:
- Gather feedback from real users who visit your website on mobile devices. Their insights can help you identify and address specific issues.
-
Consistency across Platforms:
- Ensure a consistent brand and user experience across all devices, including mobile. Users should recognize your brand and navigate your site easily whether they visit from a desktop or a mobile device.
Follow these steps and regularly monitor your website’s mobile performance. You can create a positive mobile experience for your visitors and improve your website’s visibility in mobile search results. Mobile-friendliness is increasingly important for both user satisfaction and search engine rankings.
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) Insights
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) is an open-source initiative by Google and several other companies designed to make web pages load faster on mobile devices. When implementing AMP on your website, monitoring and analyzing its performance and impact is essential.
Here are some insights you can gain by using AMP and monitoring its effectiveness:
-
Page Load Speed Improvement:
- The primary goal of AMP is to accelerate the loading speed of web pages on mobile devices. You can use performance metrics and tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to measure the improvement in page load times after implementing AMP.
-
Improved User Experience:
- Faster loading times lead to a better user experience. Monitoring user engagement metrics like bounce rates, time on page, and conversion rates can help you understand how AMP positively impacts the user experience.
-
Mobile Search Rankings:
- Implementing AMP can improve your mobile search rankings, as Google favors fast-loading pages in mobile search results. Regularly check your site’s performance in mobile search rankings to assess the impact of AMP.
-
Traffic and Click-Through Rates:
- Analyze the mobile traffic your website receives and the click-through rates (CTR) on AMP-enabled pages. If you see an increase in traffic and CTR, It is a positive indication that users are responding well to your AMP content.
-
Tracking AMP-Specific Analytics:
- Use AMP analytics tools to gather insights specific to your AMP pages. This includes metrics like pageviews, unique visitors, and interactions with your AMP content.
-
Content Performance:
- Track which types of content, like articles, videos, or product pages, perform best in AMP format. This can guide your content strategy for AMP.
-
Conversion Rate Optimization:
- If your website aims to drive conversions, monitor the conversion rates for AMP-enabled pages. Ensure the user journey from landing on an AMP page to completing a conversion is smooth.
-
Content Engagement:
- Examine how users engage with your content on AMP pages. Monitor metrics like scroll depth, interactions with multimedia elements, and the number of shares or comments.
-
Error Tracking:
- Keep an eye on the AMP-specific errors and issues reported in Google Search Console or other AMP validation tools. Regularly resolve any issues to maintain AMP compliance.
-
Cross-Device Compatibility:
- While AMP is designed for mobile devices, ensure that your AMP-enabled pages also function correctly on other devices like tablets and desktops.
-
A/B Testing:
- Conduct A/B tests to compare the performance of AMP pages with non-AMP pages. It can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of AMP on specific content types or user segments.
-
Feedback from Users:
- Collect feedback from mobile users to understand their experience with AMP pages. User insights can reveal any pain points or areas for improvement.
You need to consistently monitor these aspects and use analytics tools to gain valuable insights into the impact of AMP on your website’s mobile performance and overall user experience. These insights will help you fine-tune your AMP strategy and content to give your audience a faster and more engaging mobile experience.
Security and Manual Actions
Regarding website security and manual actions, it is essential to understand how they are related and how they can affect your website’s search engine rankings and overall online presence.
Let’s explore these concepts:
-
Website Security:
Website security is a critical aspect of maintaining a healthy online presence. And that ensures the protection of both your site and your users. Here are some key security considerations:
- SSL Certificate: Ensure your website has a valid SSL certificate (HTTPS). It helps secure data transmission and builds trust with users.
- Regular Updates: Keep your content management system (CMS), plugins, and themes up to date to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Firewalls: Implement web application firewalls (WAF) to protect your site from malicious traffic and attacks.
- Strong Passwords: Use strong and unique passwords for your website’s admin accounts and encourage users to do the same.
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up your website to recover quickly in case of a security breach.
- Security Plugins: Consider using Security Plugins or services to monitor and protect your site from threats.
-
Manual Actions:
In the context of Google Search, manual actions refer to actions taken by Google’s Search Quality Team when they identify issues with a website’s content or practices that violate Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. These actions can result in a website being penalized, and the site’s rankings in search results may suffer.
Common Reasons for Manual Actions:
- Thin or Duplicate Content: Content that offers little value to users or is copied from other sources.
- Keyword Stuffing: Overusing keywords in an attempt to manipulate search rankings.
- Unnatural Link Building: Acquiring backlinks through spammy or manipulative practices.
- Cloaking: Serving content to search engines different from what is presented to users.
- User-Generated Spam: Not adequately moderating and managing user-generated content, resulting in spammy content on your site.
-
How Security and Manual Actions Relate:
Ensuring the security of your website is crucial because security vulnerabilities can potentially lead to manual actions by search engines. For prodigitalweb, if your site is hacked and malicious content or links are injected, it may trigger manual actions from search engines. These actions can negatively impact your site’s rankings and visibility.
Conversely, addressing security issues promptly and effectively can help you avoid manual actions and maintain a strong online presence. Regular security audits, updates, and monitoring can help prevent security breaches that could lead to penalties.
-
Best Practices:
To maintain a secure and search-engine-friendly website:
- Regularly audit your website for security vulnerabilities.
- Keep your website software up to date.
- Implement security measures like firewalls and strong passwords.
- Monitor for signs of hacking and address them promptly.
- Familiarize yourself with Google’s Webmaster Guidelines and ensure your website complies with them.
By prioritizing both website security and compliance with search engine guidelines, you can protect your website from manual actions and maintain a positive online presence. If you receive a manual action notification, take it seriously. And work on it to correct the issues promptly to restore your website’s rankings.
Monitoring for Security Issues and Manual Actions
Monitoring for security issues and manual actions is crucial to maintain a healthy and secure online presence.
How to effectively monitor and address Security Issues and Manual Actions issues:
Monitoring for Security Issues:
- Regular Security Audits:
- Conduct regular security audits of your website to identify vulnerabilities and potential threats. You can use security plugins or third-party tools to automate scans for common issues.
- Update Software:
- Keep your content management system (CMS), plugins, and themes up to date. Security patches are often released to address vulnerabilities. Timely updates are essential.
- Firewall Protection:
- Implement a web application firewall (WAF) to protect your site from common security threats like DDoS attacks and SQL injection.
- Security Plugins:
- Use security plugins or services that monitor your website for suspicious activities, malware, and unauthorized access. These tools can alert you to potential issues.
- Strong Passwords:
- Ensure that you and your users use strong, unique passwords. Encourage the use of password managers to create and store secure passwords.
- Regular Backups:
- Regularly back up your website to quickly restore it in case of a security breach. Store backups in secure locations.
- Security Alerts:
- Set up security alerts or notifications to inform you of any unusual activities, login attempts, or unauthorized changes to your website.
- Monitoring Services:
- Consider using website monitoring services that offer real-time security checks and alerts.
Monitoring for Manual Actions:
- Google Search Console:
- Regularly monitor your website’s performance in Google Search Console. It provides valuable information about how your site is indexed and if any manual actions have been applied.
- Manual Action Notifications:
- Keep an eye on your email for notifications from Google Search Console. Google will inform you if manual actions are taken against your site.
- Manual Action Review:
- Review the details and reasons provided if you receive a manual action notification. Understand the issues that led to the action.
- Addressing Manual Actions:
- After identifying the issue, take corrective action immediately. This may involve fixing content, removing spammy links, or resolving other compliance issues.
- Reconsideration Request:
- If you have addressed the issues that led to the manual action, submit a reconsideration request through Google Search Console. Explain the steps you have taken to rectify the problem and request a review.
- Follow Guidelines:
- Familiarize yourself with Google’s Webmaster Guidelines and adhere to them. Avoid practices that could lead to manual actions.
- Regular Content Review:
- Periodically review your website’s content to ensure it complies with search engine guidelines. Check for thin, duplicate, or low-quality content.
- Link Profile Maintenance:
- Monitor your website’s backlink profile to ensure it is free from spammy or unnatural links. Disavow harmful links if necessary.
- User-Generated Content:
- If your site allows user-generated content, implement strong moderation and anti-spam measures to prevent low-quality or spam submissions.
By proactively monitoring for both security issues and manual actions, you can protect your website from potential threats and maintain a robust online presence. Regular audits, timely responses, and adherence to best practices are primary to ensuring the security and compliance of your website.
How to Request a Review
Requesting a review, often referred to as a “reconsideration request,” is typically used in the context of Google Search Console when your website has received a manual action or penalty from Google. Do the following steps to request a review and potentially have the penalty lifted.
-
Access Google Search Console:
- Log in to your Google Search Console account.
-
Navigate to the Manual Actions Section:
- Select the property (website) that has received the manual action.
- Click “Security & Manual Actions” in the left sidebar and choose “Manual Actions.”
-
Review the Manual Action Details:
- You will see a list of any manual actions applied to your site. Click on the specific action to view the details. Understand the reason for the action and the actions required to address it.
-
Address the Issue:
- Before submitting a reconsideration request, ensure you have thoroughly addressed the issue that led to the manual action. For prodigitalweb, disavow or remove those links if it was due to spammy backlinks. If it was due to thin content, improve the content quality.
-
Prepare a Detailed Reconsideration Request:
- Click the “Request Review” button to initiate the reconsideration process.
- In the reconsideration request form, explain your actions to rectify the issue. Be clear and transparent in your communication.
- Describe the specific changes you have made to your website or content to comply with Google’s guidelines.
- If the manual action was related to backlinks, explain how you have addressed the issue, whether you have removed problematic links or submitted a disavow file.
- If it was content-related, highlight the changes made to improve the quality and relevance of your content.
-
Submit the Reconsideration Request:
- After providing all necessary information, submit your reconsideration request.
-
Monitor Progress:
- Google’s team will review your request and your website. This process may take some time, so be patient.
- You can track the progress of your request within Google Search Console. Google may communicate with you through this platform if additional information is required.
-
Wait for a Response:
- Google will respond to your reconsideration request, indicating whether they have accepted your changes and lifted the manual action or if further improvements are needed.
-
Continue Improving:
- If your request is approved, maintain your website’s compliance with Google’s guidelines to avoid future manual actions.
- If the request is not approved, review Google’s response carefully and make the necessary improvements.
-
Resubmit if Needed:
- If your request is not approved and you believe you have addressed the issues, you can submit another reconsideration request after further improvements.
The reconsideration request process is essential for resolving manual actions and restoring your website’s search engine rankings. To increase your chances of success, ensure your request is comprehensive and provides clear evidence of your efforts to address the issue. Remember to adhere to Google’s guidelines to maintain a healthy and compliant website.
Performance Enhancements
Performance enhancements for your website are crucial for providing a fast and efficient user experience. It can improve search engine rankings. Further, it can increase user satisfaction. Here are some key performance enhancements you can implement.
-
Website Speed Optimization:
- Compress Images: Use image compression tools to reduce the file size of images without sacrificing quality.
- Minimize HTTP Requests: Combine multiple CSS and JavaScript files and minimize the use of external resources to reduce the number of HTTP requests.
- Browser Caching: Enable browser caching to store static assets locally on users’ devices. That can reduce load times for returning visitors.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): Use a CDN to serve content from servers located closer to the user, improving load times.
- Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading for images and other elements to load content as the user scrolls. Lazy loading can reduce initial page load times.
-
Mobile Optimization:
- Ensure your website is responsive and mobile-friendly. Follow mobile SEO best practices to enhance performance on mobile devices.
-
Content Optimization:
- Remove Unused or Redundant Content: Eliminate outdated or redundant content and media files to reduce the size of your website.
- Optimize Images: Properly size and compress images for web use.
- Minimize Redirects: Limit the use of redirects as they can slow down the loading process.
- Limit Third-Party Plugins: Reduce reliance on third-party plugins, scripts, or widgets that can negatively impact performance.
-
Code Efficiency:
- Minify HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Minify your code to remove unnecessary characters, white spaces, and line breaks.
- Reduce Server Requests: Minimize server requests by optimizing database queries and using efficient code.
-
Hosting and Server Optimization:
- Choose a Reliable Hosting Provider: Opt for a hosting provider with fast server performance and a good uptime reputation.
- Upgrade Server Resources: If your site experiences high traffic, consider upgrading to a more powerful server or hosting plan.
- Content Management System (CMS) Optimization: Ensure your CMS is updated and well-optimized for speed and performance.
-
Content Delivery:
- Content Caching: Implement content caching to store frequently accessed pages and serve them faster.
- Static Site Generation: Consider converting parts of your website to a static site to reduce server load and improve load times.
-
Performance Testing:
- Regular Performance Testing: Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or Pingdom to regularly test your website’s performance and identify areas for improvement.
-
Monitor and Troubleshoot:
- Monitoring Tools: Set up website monitoring tools to track performance and receive alerts if issues arise.
- Error Logs: Monitor error logs and address recurring issues impacting performance.
-
HTTPS Implementation:
- Use HTTPS for secure data transfer. Secure sites are often favored in search engine rankings.
-
Content Delivery Strategy:
- Optimize your content delivery strategy by serving critical content first and deferring non-essential elements.
-
Implement AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages):
- Consider using AMP for mobile content to provide lightning-fast loading times on mobile devices.
-
Mobile-First Design:
- Prioritize mobile design and optimization, as Google uses mobile-first indexing.
Implement these performance enhancements so that you can significantly improve the speed and efficiency of your website. That can enhance user experience and potentially achieve better search engine rankings. Regularly monitoring and fine-tuning your site’s performance is essential for maintaining a competitive online presence.
Page Speed Insights
Google PageSpeed Insights is a free online tool provided by Google that helps website owners and developers assess the performance and speed of web pages on both desktop and mobile devices. The tool provides insights and recommendations for optimizing web page loading times. Here is how to use Google PageSpeed Insights:
-
Access PageSpeed Insights:
Visit the Google PageSpeed Insights website at https://developers.google.com/speed/pagespeed/insights/.
-
Enter the URL:
Enter the web page URL you want to analyze into the search bar on the PageSpeed Insights homepage.
-
Click “Analyze”:
Click the “Analyze” button to start the assessment.
-
Review the Page Analysis:
Google PageSpeed Insights will analyze the web page’s performance. It provides a detailed report with insights and recommendations. The report is divided into two sections:
- Mobile Performance: This section focuses on how well the page performs on mobile devices.
- Desktop Performance: This section assesses the page’s performance on desktop computers.
You will see an overall performance score for each section based on Google’s Lighthouse performance scoring system. The score ranges from 0 to 100, with a higher score indicating better performance.
-
Review Opportunities and Diagnostics:
The report includes opportunities and diagnostics. These are specific recommendations to improve your web page’s performance. These may include:
- Optimize Images: Suggestions to reduce image file sizes or use next-gen image formats.
- Leverage Browser Caching: Recommendations to enable browser caching for static assets.
- Eliminate Render-Blocking Resources: Suggestions to minimize the impact of render-blocking CSS and JavaScript.
- Minimize Main-Thread Work: Recommendations to reduce main-thread work and make pages more responsive.
Each recommendation provides details and links to additional resources for making the necessary improvements.
-
Test on Different Devices:
You can use the dropdown menu at the report’s top to switch between mobile and desktop views. It allows you to evaluate performance on both device types.
-
Reanalyze and Verify Changes:
After optimizing your web page based on the recommendations provided, you can return to PageSpeed Insights and reanalyze the page to see if the changes have improved performance.
PageSpeed Insights is a valuable tool for understanding how well your web pages are optimized for speed and user experience. Following its recommendations, regularly test and optimize your website. So that you can enhance page load times. In addition, you can improve user satisfaction and potentially boost your search engine rankings.
Core Web Vitals and their impact on SEO
Core Web Vitals are a set of specific web performance metrics that Google considers essential for user experience. These metrics assess web pages’ loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability. Core Web Vitals have become a critical factor in Google’s ranking algorithm. And they can impact your website’s SEO and search engine rankings. Here is an overview of the Core Web Vitals and their impact on SEO:
-
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP):
- What it measures: LCP evaluates the loading performance of the largest content element on a web page, like an image or text block.
- Impact on SEO: LCP is a crucial metric for user experience. A fast LCP indicates that users can access the main content quickly. That is leading to higher user satisfaction. Google rewards websites with fast LCP with better rankings.
-
First Input Delay (FID):
- What it measures: FID gauges the interactivity of a web page. It measures the delay between a user’s first interaction (clicking a button) and the browser’s response.
- Impact on SEO: FID is critical for user engagement. A low FID ensures that users can interact with your site smoothly. That can lead to longer dwell times and more positive signals to search engines.
-
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS):
- What it measures: CLS quantifies the visual stability of a web page. It assesses how often page elements shift unexpectedly while the page is loading.
- Impact on SEO: CLS is important for user experience. A lower CLS means users are less likely to click on the wrong elements due to layout shifts accidentally. That is resulting in fewer frustration-related bounce-backs and better user satisfaction.
Impact on SEO:
Core Web Vitals have a direct impact on SEO for several reasons:
- Ranking Signal: Google has incorporated Core Web Vitals as a ranking signal. As measured by these metrics, websites that provide better user experiences can expect a positive impact on their search engine rankings.
- User Satisfaction: Sites with fast loading times, smooth interactivity, and minimal layout shifts tend to have higher user satisfaction. Satisfied users are likelier to engage with your content and stay on your site longer. And that can indirectly boost your SEO.
- Mobile Optimization: Mobile-friendliness is closely related to Core Web Vitals, as mobile devices have stricter performance requirements. Google’s mobile-first indexing strategy also emphasizes the importance of mobile user experience. And that aligns with these vitals.
- Page Experience Update: Google’s Page Experience Update incorporates Core Web Vitals as a ranking factor. Websites that meet these criteria may have an advantage in search results.
To improve your SEO by optimizing for Core Web Vitals:
- Analyze your site’s performance using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, or web.dev.
- Address performance issues and follow recommendations to improve LCP, FID, and CLS.
- Regularly monitor your site’s performance to ensure ongoing optimization.
- Invest in responsive web design, optimized images, efficient coding, and content delivery networks (CDNs) to enhance web performance.
Prioritizing Core Web Vitals can provide a better user experience to enhance your site’s SEO, user engagement, and overall search engine rankings.
Enhancing Site Links with Structured Data
Enhancing site links with structured data is a strategy that can improve the visibility and attractiveness of your website’s search results in Google. Structured data, also known as schema markup, provides search engines with additional context about the content on your pages. This, in turn, can lead to the creation of rich site links, also known as “rich snippets.” That offers more information to users. And it potentially increases click-through rates. Here is how to enhance site links with structured data:
-
Identify Relevant Content:
Determine which pages on your website contain content that could benefit from structured data. These could include product pages, articles, reviews, events, or any content with specific attributes you want to highlight.
-
Implement Schema Markup:
Add structured data to the HTML of your web pages. You can specify the structured data using various schema markup formats, like JSON-LD, microdata, or RDFa. Popular schemas include:
- Product: For e-commerce sites, you can mark up product information like name, price, availability, and ratings.
- Article: Use this schema for news articles, blog posts, or other written content.
- Event: Mark up details like date, time, location, and ticket information.
- Review: To showcase user reviews and ratings for products or services.
- FAQ: For frequently asked questions, answers, and question topics.
-
Test the Markup:
Use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool or the Rich Results Test to ensure your schema markup is valid and correctly implemented. Fix any issues or errors that are identified during the testing process.
-
Submit Your Sitemap:
Submit your website’s XML sitemap to Google Search Console. This helps Google discover and index the structured data on your pages more efficiently.
-
Monitor Search Results:
Keep an eye on your site’s search results to see if Google starts displaying rich site links for your content. This may take some time, as Google needs to re-crawl and re-index your pages.
-
Optimize for Rich Snippets:
To enhance your chances of obtaining rich site links, consider these additional strategies:
- Ensure your content is high-quality and valuable to users.
- Use clear and descriptive page titles and Meta descriptions.
- Include relevant, high-resolution images on your pages. That may appear in rich snippets.
- Encourage user-generated reviews and ratings for products or services.
- Keep your structured data current, especially for event details and product information.
-
Leverage Other Rich Results:
In addition to site links, you can use structured data to obtain rich results like recipe snippets, FAQ snippets, or event snippets. The richer the results you can obtain, the more attractive and informative your search results will be.
Implement structured data and optimize your website for rich site links. You can provide users with more valuable information in search results and potentially increase click-through rates. Ultimately, it is improving your website’s visibility and traffic.
Utilizing Structured Data for Rich Results
Utilizing structured data for rich results can significantly enhance your website’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs). And it improves the click-through rate by providing users with more informative and visually appealing search results. Here are steps to effectively utilize structured data for rich results.
-
Choose Relevant Schema Markup:
Determine the appropriate schema markup for the type of content on your website. Common structured data types include:
Article: For news articles, blog posts, and other textual content.
Product: Ideal for e-commerce sites to showcase detailed product information.
Recipe: Used to display cooking recipes with ingredients and instructions.
Event: For promoting events, concerts, conferences, and more.
FAQ: To present frequently asked questions and answers.
Local Business: For physical businesses, provide key details like name, address, and contact information.
Review: Highlight user reviews and ratings for products or services.
-
Implement Schema Markup:
Add structured data to your web pages using a supported markup format like JSON-LD, microdata, or RDFa. Typically, JSON-LD is recommended because it is easy to implement and maintain. Include the structured data in the HTML of the page.
Here is a prodigitalweb of JSON-LD structured data for a “Product”:
-
Test the Markup:
Use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool or the Rich Results Test to ensure your schema markup is valid and correctly implemented. These tools will help you identify and fix any issues with your structured data.
-
Monitor Google Search Console:
After implementing structured data, log in to Google Search Console and check for any errors or issues related to your structured data. Google Search Console provides valuable insights into how Google interprets and uses your schema markup.
-
Submit a Sitemap:
Submit your website’s XML sitemap to Google Search Console. This helps Google discover and index your structured data more efficiently.
-
Ensure High-Quality Content:
Structured data alone will not guarantee rich results. Your content should be of high quality and relevant to users. Rich results are more likely for valuable content, like informative articles or comprehensive product descriptions.
-
Encourage User Engagement:
Some structured data types, like reviews, encourage users to leave reviews and ratings for your products or services. Positive reviews can enhance the appeal of your search results.
-
Optimize for Visual Content:
Utilize high-quality and relevant images whenever possible, as they may be included in rich results. Make sure your images are properly formatted and optimized.
-
Keep Structured Data Up-to-Date:
Regularly update your structured data to ensure that it accurately reflects the content on your website. This is particularly important for event information, product availability, and pricing.
-
Monitor and Iterate:
Regularly check your search results and rich snippets. Adjust your structured data and content based on user engagement and performance data.
Effectively utilize structured data for rich results. You can enhance the presentation of your content in search results. And that can provide users with more context and information. And it potentially increases click-through rates. Besides, it improves your website’s visibility and performance in search engines.
How to implement structured data on your site
Implementing structured data on your website involves adding specific markup to your HTML code. It provides search engines with additional context about the content on your pages. This structured data helps search engines understand your content better and can lead to the creation of rich snippets in search results.
How to implement structured data on your site:
-
Choose the Appropriate Schema Markup:
Determine which schema markup is suitable for the type of content on your website. You can browse the schema.org website to find your content’s most relevant schema types. Common schema types include “Article,” “Product,” “LocalBusiness,” “Review,” and more.
-
Create the Structured Data Markup:
Customize the content within the script tag to match the information for your specific content type.
-
Add the Structured Data to Your HTML:
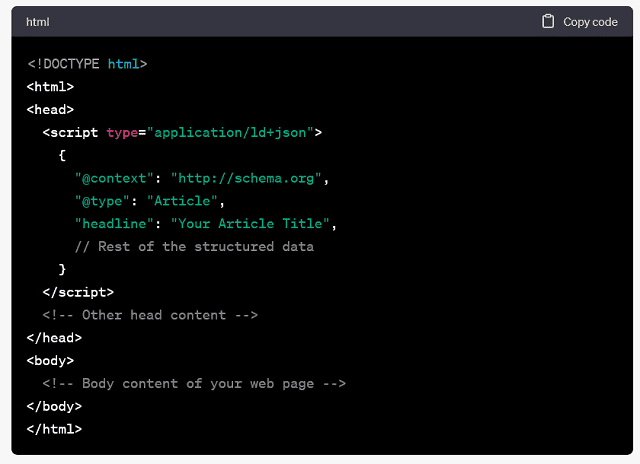
-
Validate Your Structured Data:
Before deploying the structured data to your live website, validate it using Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool (https://search.google.com/structured-data/testing-tool/) or the Rich Results Test (https://search.google.com/test/rich-results). These tools will help you identify any errors or issues with your structured data.
-
Test Implementation:
Inspect the page source code and check if the structured data is correctly implemented. Ensure there are no syntax errors or issues with the JSON-LD markup.
-
Monitor and Maintain:
After implementing structured data, monitor your search results in Google to see if rich snippets or enhanced search results appear for your pages. Regularly review and update your structured data, especially if your content or offerings change.
Implement structured data on your website to provide search engines with valuable context about your content. It increases the likelihood of your content being presented as rich snippets in search results. This can improve your website’s visibility and click-through rates. It enhances the user experience and SEO performance.
International Targeting and Site Settings
International targeting and site settings are crucial to your website’s SEO and user experience. That is especially true if your business or website caters to a global or multilingual audience. These settings help search engines understand your content’s geographical and language preferences. That can impact your search engine rankings and user engagement.
Steps to Effectively Configure International Targeting and Site Settings:
-
Set Geographic Targeting in Google Search Console:
Google Search Console provides a tool for specifying the geographic target for your website. To set your site’s geographic target:
- Log in to your Google Search Console account.
- Select your property (website).
- In the left sidebar, click “Settings” under “Legacy tools and reports.”
- Click on “International Targeting.”
- In the “Country” tab, select the country or countries you want to target. Choose “Unlisted” if you will target a global audience without specifying a single country.
-
Use Hreflang Tags:
Hreflang tags are HTML Meta tags that signal your content’s language and regional targeting to search engines. Use them to improve the accuracy of search engine rankings for specific languages or regions. For prodigitalweb, you might use hreflang tags to differentiate between English content for the United States and English Content for the United Kingdom.
-
Implement Subdirectories or Subdomains:
For multilingual websites, you can organize your content using subdirectories (/en/ for English, /es/ or Spanish) or subdomains (en.prodigitalweb.com, es.prodigitalweb.com) to indicate different language versions. Make sure to use clear, user-friendly URLs for each version.
-
Create Sitemaps for Each Language or Region:
Generate separate sitemaps for each language or region to help search engines understand the structure and content of your multilingual website.
-
Optimize Content for Local Keywords:
If you have a regional or local audience, conduct keyword research for the specific region or country you are targeting. Optimize your content with region-specific keywords and phrases.
-
Ensure Consistent User Experience:
Provide a consistent user experience across language versions. This includes maintaining similar page structures, navigation, and branding to keep the user experience cohesive.
-
Use Language and Region Tags in HTML:
Use language and region tags in your HTML code to specify your website’s language and regional settings. For prodigitalweb:

-
Monitor International SEO Performance:
Regularly review your international SEO performance in Google Search Console. Keep an eye on the search queries and countries generating traffic and clicks. This data can inform your optimization efforts.
-
Test Your Site’s User Experience:
Ensure that your website is accessible and user-friendly for visitors from different regions and language backgrounds. Test navigation, load times, and responsiveness on various devices.
-
Localize Content When Necessary:
For international audiences, consider localizing your content to provide culturally relevant information. This may include currency and measurement conversions, address formats, and other local customs.
Configuring international targeting and site settings is essential for attracting and retaining a diverse and global audience. Properly optimizing your website for different languages and regions can help you reach a wider audience. And that improves user engagement. And it enhances your search engine rankings in specific regions and languages.
Setting Geotargeting Preferences
Setting geotargeting preferences is essential when you want to specify the geographical target or location of your website’s content. Geotargeting is particularly important if your website is intended for a specific country, region, or audience.
Steps to Set Geotargeting Preferences:
-
Google Search Console:
Google Search Console allows you to specify your website’s geographic target. Follow these steps:
- Log in to your Google Search Console account.
- Select the property (website) you want to set geotargeting for.
- In the left sidebar, click “Settings” under “Legacy tools and reports.”
- Click on “International Targeting.”
- In the “Country” tab, you can specify the country or region you want to target. Choose “Unlisted” if you will target a global audience without setting a single country.
-
Bing Webmaster Tools:
You can use Bing Webmaster Tools to set geotargeting preferences for Bing and Yahoo! search engines. Here is how:
- Log in to your Bing Webmaster Tools account.
- Select your website.
- In the left navigation menu, click on “Configure My Site.”
- Click on “Geotargeting” to specify your website’s country or region.
-
Hreflang Tags:
Hreflang tags are essential for specifying your content’s language and regional targeting. They help search engines understand the relevance of your pages to different locations. To implement hreflang tags:
- In the HTML of each page, include the hreflang tag with the appropriate language and region code. For prodigitalweb:
- Ensure you have the equivalent content in the specified languages or regions on separate pages.
-
Subdirectories or Subdomains:
Organize your content into subdirectories (/en/ for English, /fr/ for French) or subdomains (en.prodigitalweb.com, fr.prodigitalweb.com) to indicate different language versions or regional content. This helps search engines understand the geographical and language targeting of your content.
-
Sitemaps:
Generate separate XML sitemaps for each language or region to help search engines correctly crawl and index your content. Submit these sitemaps to Google and Bing Webmaster Tools.
-
Content Localization:
For geotargeting specific regions or countries, consider localizing your content. This may involve adapting content to the local culture, currency, and regional nuances.
-
Monitor and Adjust:
Regularly monitor your website’s performance in search results and analyze user behavior. Make adjustments based on your findings to ensure your geotargeting preferences are effective.
Setting geotargeting preferences is crucial for reaching your intended audience and ensuring the content appears in search results relevant to specific regions or languages. It is essential to keep your geotargeting settings up-to-date and aligned with your content strategy as your website evolves.
Managing Domain and URL Parameters
Managing domain and URL parameters is crucial for maintaining the SEO and user-friendliness of your website. By carefully configuring your Domain and handling URL parameters, you can improve your website’s ranking in search engines, enhance user experience, and ensure that your content is effectively crawled and indexed. Here are some best practices for managing domain and URL parameters:
-
Managing Domain
- Choose a Consistent Domain Name: Opt for a single, consistent domain name for your website (prodigitalweb.com or prodigitalweb.com). Avoid having multiple variations (with or without “www”) to prevent duplicate content issues.
- Set up Proper Canonicalization: Use canonical tags to specify the preferred version of your Domain. For instance, if your website is accessible via “www” and non-www versions, set up a canonical tag to specify the preferred version.
- Utilize 301 Redirects: If you change your Domain or migrate content to a new domain, use 301 redirects to inform search engines and users about the permanent move. This helps transfer the SEO value from the old Domain to the new one.
-
Handling URL Parameters
- Specify Parameters in Google Search Console: You can configure how Googlebot handles URL parameters in Google Search Console. This is particularly useful for e-commerce websites with sorting and filtering options and dynamic content.
- Implement Canonical Tags: Use canonical tags on pages with URL parameters. This consolidates the ranking signals for pages with similar content but different parameters.
- Set Noindex for Duplicate Content: If URL parameters create duplicate content issues, set “noindex” Meta tags on those pages to prevent them from being indexed.
- Use the Robots.txt File: You can block search engines from crawling specific URLs or directories with URL parameters using the robots.txt file. Be cautious with this method, as it can also block legitimate content.
- Implement the Rel=prev/next Attribute: If you have paginated content (product pages or articles split into multiple pages), use the rel=”prev” and rel=”next” attributes to indicate the pagination sequence and help search engines understand the relationship between pages.
- Utilize the “URL Parameters” Tool in Google Search Console: Google Search Console provides a tool to manage URL parameters. You can specify how Googlebot should handle various parameters, whether to crawl, index, or ignore them.
-
Test and Monitor:
- Regularly test and monitor how search engines handle your website’s URLs and parameters. Pay attention to indexation and ranking changes.
- Use Google’s URL Inspection tool in Search Console to check how Googlebot sees your pages.
- Monitor your website’s performance, user behavior, and errors through Google Analytics and Google Search Console.
-
Minimize URL Parameters:
- If possible, aim to reduce the number of URL parameters used on your site. Keep URLs clean and simple for users and search engines.
Managing domain and URL parameters is an ongoing process that requires close attention and adjustments as your website evolves. Properly configuring your Domain and handling URL parameters ensures that your site is SEO-friendly, user-friendly, and effectively understood by search engines. That will lead to better rankings and user experience.
Integration with Google Analytics
Integrating your website with Google Analytics is essential for tracking and analyzing visitor behavior, engagement, and website performance. Google Analytics provides valuable insights into your website’s traffic sources, user demographics, and user behavior. Google Analytics helps you make data-driven decisions to improve your online presence.
Steps To Integrate Your Website With Google Analytics:
-
Create a Google Analytics Account:
If you still need a Google Analytics account, visit the Google Analytics website (https://analytics.google.com/). Sign in with your Google account or create a new one. Follow the steps to set up your account and property (your website).
-
Set Up a Property:
Once you have created your Google Analytics account, you need to set up a property for your website. Here is how:
- Click on the “Admin” tab.
- Under the “Account” column, select the account you created (or create a new account).
- Under the “Property” column, click “Create Property.”
- Choose “Web” as the type of property.
- Enter your website’s URL, property name, industry category, and reporting time zone.
-
Get Your Tracking Code:
After setting up your property, you will receive a unique tracking code snippet. This code must be added to your website’s HTML code to collect data. Here is how to obtain the tracking code:
- In your property settings, navigate to the “Tracking Info” section.
- Click on “Tracking Code.”
- Copy the tracking code provided. It will look similar to:
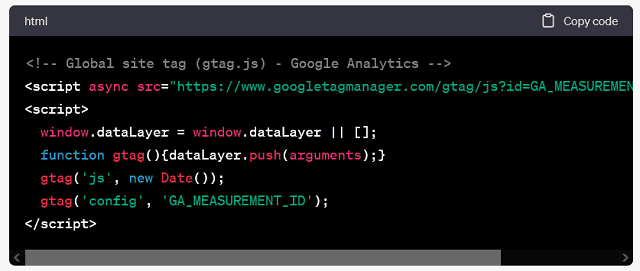
-
Add the Tracking Code to Your Website:
To add the tracking code to your website, follow these steps:
- Paste the tracking code snippet just before the closing </head> tag of your website’s HTML code. This typically goes in the header section of your site.
- For websites built with a content management system (CMS) like WordPress, you can use plugins or settings provided by the CMS to insert the tracking code without editing the HTML directly.
-
Verify the Tracking Code:
After adding the tracking code, verify its implementation to ensure it works correctly. You can use the Google Tag Assistant browser extension to check if the code is firing as expected.
-
Wait for Data to Accumulate:
It may take a few hours or up to 24 hours for Google Analytics to start collecting and displaying data. Once data starts flowing, you can access various reports and insights through the Google Analytics dashboard.
-
Configure Goals and Custom Reports:
Set up goals and custom reports in Google Analytics to track user interactions like form submissions, purchases, or other conversions relevant to your website’s objectives.
-
Use Google Analytics:
Regularly analyze the data from Google Analytics to gain insights into your website’s performance, user behavior, traffic sources, and other key metrics. Use these insights to make informed decisions about optimizing your website.
Integrating Google Analytics with your website gives valuable insights into your site’s performance and user behavior. This data helps you make data-driven decisions to improve your website. It enhances user experience and achieves your online goals.
Combining Google Search Console data with Google Analytics
Combining Google Search Console data with Google Analytics can give you a more comprehensive view of your website’s performance, user behavior, and search engine optimization efforts. This integration allows you to correlate search engine data with user engagement metrics, helping you make informed decisions to improve your website’s visibility and user experience. Here is how to combine Google Search Console data with Google Analytics:
-
Link Google Search Console and Google Analytics:
Before combining the data, you must link your Google Search Console account with your Google Analytics account. Here is how to do it:
- Log in to your Google Analytics account.
- In the property where you want to link Search Console data, go to the “Admin” section.
- Under the property column, select the property you want to link to Search Console data.
- In the “Property” column, click on “All Products.”
- In the “Search Console” section, click on “Link Search Console.”
- Choose the site you want to link from the list and click “Add.”
- Click “Save.”
-
Enable Data Sharing:
After linking the accounts, you may need to enable data sharing between Google Analytics and Search Console. To do this:
- In the “Admin” section of Google Analytics, navigate to your property settings.
- Under “Product Linking,” select “All Products.”
- Make sure that “Google Search Console” is enabled.
-
Access Combined Data:
Once the accounts are linked, and data sharing is enabled, you can access the combined data in Google Analytics. Here are a few ways to explore the data:
- Acquisition Reports: In Google Analytics, navigate to “Acquisition” > “Search Console” to view data related to your website’s performance in search results. You can see clicks, impressions, click-through rate (CTR), and average position.
- Behavior Reports: Check the “Landing Pages” report to see which pages attract organic search traffic. You can understand how users interact with these pages by examining metrics like bounce rate and time on the page.
- Queries Report: The “Queries” report shows which search terms drive traffic to your site. This can help you identify valuable keywords and content opportunities.
-
Create Custom Reports:
You can also create custom reports in Google Analytics to combine data from the Search Console with other relevant metrics. This can give you a more holistic view of your website’s performance. For prodigitalweb, you might create a custom report that shows organic search traffic alongside e-commerce conversion data.
-
Set Up Goals and Conversions:
Utilize Google Analytics goals and e-commerce tracking to measure how organic search traffic contributes to your website’s objectives, like form submissions, purchases, or other conversions. This allows you to evaluate the impact of search engine optimization efforts on your business goals.
-
Monitor Over Time:
Keep an eye on the combined data over time to identify trends, opportunities, and areas that need improvement. Regular monitoring enables you to make informed decisions to enhance your website’s performance and user experience.
Combining Google Search Console data with Google Analytics can help you gain deeper insights into your website’s performance in search results and how users interact with your site. This valuable data allows you to make data-driven decisions and optimize your website for better results.
Analyzing user behavior and search performance together
Analyzing user behavior and search performance together can provide valuable insights into how your website is performing in search engines. It shows how visitors engage with your content. Combining data from Google Search Console and Google Analytics gives you a holistic view of your website’s SEO and user experience.
How to Analyze User Behavior and Search Performance Together:
-
Access the Data:
First, ensure you have linked your Google Search Console and Google Analytics accounts, as mentioned in a previous subheading. Once your accounts are linked, you can access the combined data in Google Analytics.
-
Review Organic Search Traffic:
Navigate to Google Analytics, and under “Acquisition,” select “All Traffic” and then “Channels.” You can filter the data by choosing “Organic Search.” This provides an overview of the organic search traffic to your website.
-
Explore User Behavior Metrics:
With your organic search traffic data in view, you can now analyze user behavior metrics. Here are key user behavior metrics to consider:
- Bounce Rate: This metric indicates the percentage of users who visited a single page on your site and then left without taking any further action. A high bounce rate may suggest a poor user experience.
- Pages per Session: It shows the average number of pages a user views during a session. A higher number indicates that users are engaging more with your content.
- Average Session Duration: This metric reflects users’ average time on your site. Longer sessions typically indicate more engaged users.
- Conversion Rate: You can monitor the conversion rate if you set up goals or track e-commerce. The conversion rate shows the percentage of users who completed a desired action, like filling out a contact form or purchasing.
-
Analyze Landing Pages:
To understand how users behave after arriving at search results, go to “Behavior” > “Site Content” > “Landing Pages” in Google Analytics. This report shows how different landing pages perform regarding user behavior metrics.
-
Compare with Search Console Data:
Next, cross-reference this user behavior data with the search performance data from Google Search Console. Here is how:
- In Google Analytics, you can access Search Console data under “Acquisition” > “Search Console.”
- Review metrics like clicks, impressions, click-through rate (CTR), and average position collected from the Search Console.
- Compare these metrics with user behavior metrics to identify patterns. For prodigitalweb, pages with higher positions in search results tend to have lower bounce rates or longer average session durations.
-
Identify Opportunities and Issues:
By comparing user behavior and search performance, you can identify opportunities and issues on your website. For prodigitalweb, if you have pages with high impressions but low click-through rates, it may indicate that you need to improve your title tags and Meta descriptions to make them more appealing to users.
-
Make Data-Driven Decisions:
Use the insights gained from the combined data to make data-driven decisions about your website’s Content, user experience, and SEO. You can develop strategies to improve rankings for underperforming pages. You can optimize your content for user engagement. And you set goals to enhance user behavior metrics.
-
Monitor progress:
Regularly monitor the combined data to track the impact of your optimization efforts. Adjust your strategies based on how users respond and your evolving search performance.
By analyzing user behavior and search performance, you can better understand how users interact with your website and how your SEO efforts impact their experience. This integrated approach allows you to fine-tune your strategies and improve your website’s overall performance and user satisfaction.
Frequently Asked Questions about Google Search Console
The FAQ about Google Search Console can help you better understand and utilize this valuable tool to improve your website’s performance in search engine results.
Here are some common questions and their answers:
-
What is GSC?
Google Search Console is a free web service provided by Google. That allows website owners and webmasters to monitor, manage, and optimize their site’s visibility in Google Search results. It provides insights into how Googlebot crawls and indexes your website.
-
How do I access Google Search Console?
You can access Google Search Console by signing in with your Google account at https://search.google.com/search-console. You will need to verify Ownership of your website to use the tool effectively.
-
Why is Google Search Console important for website owners?
GSC is crucial for website owners because it provides valuable data about how your site is performing in Google Search. It helps you identify and fix issues. It helps to improve your website’s visibility and enhance your SEO efforts.
-
What are the key features of Google Search Console?
Key features of GSC:
- Crawl and index status monitoring.
- Performance reports, including clicks, impressions, CTR, and average position.
- Index coverage reports.
- Structured data and rich snippet insights.
- Mobile usability reports.
- Security and manual actions monitoring.
- Sitemap submission and URL inspection tools.
-
How do I verify my website in Google Search Console?
You can verify your website in GSC using several methods, including HTML file upload, HTML tag insertion, domain name provider, or Google Tag Manager. Choose the method that best suits your technical capabilities and website platform.
-
How often should I check Google Search Console?
Regularly monitor GSC to stay informed about your website’s performance. Weekly or monthly checks are recommended to catch issues early and make timely optimizations.
-
How can I improve my website’s performance using Google Search Console?
GSC can help you identify and resolve issues like crawl errors, indexing problems, mobile usability issues, and more. You can also use performance data to refine your Content and SEO strategies.
-
What should I do if I receive manual actions in GSC?
If you receive manual actions, review the issues and follow Google’s guidelines for addressing them. Once you have resolved the problems, you can request a review in GSC to have the manual action lifted.
-
How can I track the performance of specific pages or keywords in Google Search Console?
Use the URL Inspection tool to check the indexing status of specific pages. And use the Performance report to track the performance of specific queries or pages over time.
-
Can I use Google Search Console for multiple websites?
You can manage multiple websites in a single Google Search Console account. Simply add properties for each site you want to monitor.
-
Is Google Search Console the same as Google Analytics?
No, Google Search Console and Google Analytics are separate tools with different purposes. GSC focuses on search engine performance. Google Analytics provides in-depth insights into user behavior on your website.
-
How can I get support for Google Search Console issues?
If you encounter problems with GSC, you can visit the Google Search Central Help Community (formerly Google Webmaster Help Forum) or contact Google’s official support for assistance.
-
Are there any costs associated with using Google Search Console?
No, Google Search Console is a free service provided by Google for website owners and webmasters to improve their website’s performance in Google Search.
Frequently Asked Questions about Google Search Console can help you navigate the tool. And you can use it effectively to optimize your website’s performance in search engine results.
Common Queries and Their Answers
Here are some common queries related to Google Search Console, along with their answers:
-
What is the purpose of Google Search Console?
Google Search Console is a web service provided by Google. It allows website owners and webmasters to monitor, manage, and optimize their website’s visibility in Google Search results. It provides insights into how Googlebot crawls and indexes your website.
-
How do I add my website to Google Search Console?
To add your website to Google Search Console, you must verify Ownership. The verification process typically involves methods like HTML file upload, HTML tag insertion, domain name provider, or Google Tag Manager. Follow the verification process that suits your technical capabilities.
-
What common issues can Google Search Console help me identify?
Google Search Console can help you identify issues like crawl errors, indexing problems, mobile usability issues, structured data errors, and security concerns like malware or phishing. It also provides insights into your website’s performance in search results.
-
How often should I check Google Search Console for updates and issues?
It is recommended to check Google Search Console regularly, at least weekly or monthly. Regular checks help you catch issues early and make timely optimizations to improve your website’s performance.
-
Can I track the performance of specific pages or keywords in Google Search Console?
Yes, you can use the URL Inspection tool to check the indexing status of specific pages. Additionally, you can use the Performance report to track the performance of specific queries or pages over time.
-
What should I do if I receive manual actions in the Google Search Console?
If you receive manual actions, review the issues and follow Google’s guidelines for addressing them. Once you have resolved the problems, you can request a review in Google Search Console to have the manual action lifted.
-
Can I use Google Search Console for multiple websites?
You can manage multiple websites in a single Google Search Console account. Simply add properties for each site you want to monitor.
-
How is Google Search Console different from Google Analytics?
Google Search Console focuses on search engine performance. It provides insights into your site’s appearance in search results and helps identify visibility issues. Google Analytics, on the other hand, provides data on user behavior on your website, including traffic sources, page views, and conversions.
-
Does using Google Search Console cost anything?
No, Google Search Console is a free service provided by Google for website owners and webmasters to improve their website’s performance in Google Search.
-
How can I get support for Google Search Console issues?
If you encounter problems with Google Search Console, visit the Google Search Central Help Community or contact Google’s official support for assistance.
These common queries and their answers can help you better understand and utilize Google Search Console to improve your website’s visibility in search engine results.
Troubleshooting Tips
Troubleshooting issues in GSC and website performance can be essential to ensure that your site is appropriately indexed and visible in Google’s search results.
The Troubleshooting Tips to Help You Address Common Problems in GSC:
-
Verify Ownership:
- If your website is not verified in GSC, ensure you have completed the verification process correctly. Double-check that the verification code is perfectly placed in your website’s HTML.
-
Check for Crawl Errors:
- Regularly review GSC’s “Coverage” report to identify crawl errors like pages not indexed, blocked resources, or server errors. Address these issues to ensure proper indexing.
-
Analyze Index Coverage Issues:
- Use the “Index Coverage” report to investigate indexing issues. Look for errors like “Submitted URL not selected as canonical” or “Crawl anomaly.” Address these issues to improve your site’s index coverage.
-
Review Manual Actions:
- Keep an eye on the “Manual Actions” report in GSC. If Google identifies manual actions taken against your site (for spam or quality issues), follow Google’s guidelines to resolve the problems and request a review.
-
Monitor Mobile Usability:
- Check the “Mobile Usability” report to ensure your website is mobile-friendly. Address any issues that may negatively impact mobile user experience.
-
Inspect URLs:
- Use the URL Inspection tool in GSC to troubleshoot individual URLs. You can see how Googlebot views a specific page, identify issues, and check if a page is indexed.
-
Test Structured Data:
- Use GSC’s “Rich Results Test” tool to validate your structured data (schema markup). Ensure it is correctly implemented and does not contain errors.
-
Investigate Security Issues:
- Monitor GSC’s “Security & Manual Actions” report to identify and address security issues like malware or phishing. Google may flag security concerns that need immediate attention.
-
Use Sitemaps:
- Ensure your sitemap is up to date and submitted in GSC. This helps Googlebot find and index your pages more efficiently.
-
Monitor Performance Data:
- Check the “Performance” report in GSC to evaluate how your website is performing in search results. Analyze clicks, impressions, click-through rate, and average position. Identify opportunities to improve search performance.
-
Test for Mobile Usability:
- Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to verify that your site is mobile-friendly. Ensure that your website is responsive and user-friendly on various mobile devices.
-
Address Page Speed:
- Slow page loading times can negatively impact your website’s performance and rankings. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to identify and address speed issues.
-
Troubleshoot Rich Snippets:
- If rich snippets are not appearing as expected in search results, review your structured data and ensure It is correctly implemented. The Structured Data Testing Tool can help identify issues.
-
Monitor Server Errors:
- Keep an eye on server error reports in GSC. Address server issues promptly to prevent them from affecting indexing and user experience.
-
Seek Community Help:
- If you encounter technical challenges, consider seeking help in Google’s official Search Central Help Community or other webmaster forums.
-
Keep an Eye on Notifications:
- Check GSC for any notifications and messages from Google regarding your website. Google may provide alerts about issues or essential updates.
-
Stay Informed:
- Regularly read Google’s Webmaster Blog and official guidelines to stay up to date on best practices and changes in search algorithms.
Troubleshooting in GSC and addressing website performance issues is an ongoing process. Regular monitoring and proactive measures can help ensure your website is well-optimized for search engines and provides a positive user experience.
Tips for Maximizing SEO Benefits with Google Search Console
GSC is a powerful tool for improving your website’s SEO. And it is enhancing its visibility in Google’s search results. To maximize the SEO benefits of GSC, consider the following tips:
-
Verify and Monitor Your Website:
- Ensure your website is correctly verified in GSC. Monitor your site regularly to detect and address issues affecting its performance in search results.
-
Utilize the Performance Report:
- The GSC performance report provides valuable insights into your website’s search performance. Analyze clicks, impressions, click-through rate (CTR), and average position to identify trends and opportunities.
-
Identify and Optimize High-Impact Pages:
- Identify high-impact pages by reviewing the performance data. Optimize these pages by improving their Content, Meta tags, and user experience to enhance their rankings.
-
Investigate Click-Through Rate (CTR):
- Analyze CTR to see how well your pages attract clicks. Optimize your page titles and Meta descriptions to make them more appealing to users.
-
Focus on Mobile Usability:
- Ensure your website is mobile-friendly. GSC’s Mobile Usability report helps you identify and fix issues that can impact your mobile rankings.
-
Check for Index Coverage Issues:
- Regularly review the Index Coverage report in GSC. Address crawl errors, indexing problems, and coverage issues to ensure your content is appropriately indexed.
-
Monitor Structured Data and Rich Results:
- Use GSC to check for structured data errors and validate your rich results. Properly implemented structured data can enhance the appearance of your search results.
-
Submit and Manage Sitemaps:
- Create and submit XML sitemaps for your website in GSC. This helps Google better understand your site’s structure and content. Ensure that your sitemaps are up-to-date.
-
Review Security and Manual Actions:
- Regularly check the GSC Security & Manual Actions report to identify and resolve security issues and manual actions. A clean site is essential for SEO.
-
Set up Performance Filters:
- Use filters in the Performance report to analyze specific queries, pages, countries, or devices. This allows you to target your SEO efforts more effectively.
-
Monitor URL Inspection:
- Use the URL Inspection tool in GSC to check how Googlebot views specific pages on your site. This can help you identify issues and ensure your pages are indexed as expected.
-
Keep an Eye on Algorithm Updates:
- Stay informed about Google’s algorithm updates and guidelines. Adjust your SEO strategies in response to changes that can impact your website’s rankings.
-
Regularly Analyze Keyword Queries:
- Use GSC to evaluate the search queries that drive traffic to your site. Identify valuable keywords and create content around them to improve rankings.
-
Seek Community Help:
- If you encounter technical challenges, consider seeking help in Google’s official Search Central Help Community or other webmaster forums.
-
Continuously Improve User Experience:
- Improving user experience on your website can indirectly benefit SEO. Make your site faster, easier to navigate, and rich in content to enhance user satisfaction.
-
Track Core Web Vitals:
- Monitor and optimize your site’s Core Web Vitals, including page speed, loading times, and visual stability. These metrics can significantly impact your site’s SEO.
By implementing these tips and regularly using Google Search Console to monitor and optimize your website’s performance, you can maximize the SEO benefits of this powerful tool and improve your site’s visibility in Google’s search results.
Utilizing GSC Data for SEO Strategy
Utilizing data from GSC for your SEO strategy is crucial for optimizing your website’s performance in search engine results. GSC provides valuable insights into how Googlebot crawls and indexes your site and how users interact with your content.
How to effectively use GSC data for your SEO strategy:
-
Monitor Search Performance:
- Use the “Performance” report in GSC to track key metrics such as clicks, impressions, click-through rate (CTR), and average position. Analyze this data to understand how your site is performing in Google Search.
-
Identify High-Impact Pages:
- Review the pages with the highest impressions, clicks, and CTR. These pages are your best performers and are ideal candidates for optimization.
-
Optimize Click-Through Rate (CTR):
- Identify pages with high impressions but low CTR. Optimize their Title Tags and Meta Descriptions to make them more compelling to users.
-
Analyze User Queries:
- Use the “Queries” report to understand which search queries bring users to your site. Identify valuable keywords and phrases to target in your content.
-
Address Crawl and Index Issues:
- Regularly check the “Index Coverage” report for crawl errors and indexing problems. Address these issues to ensure Google can access and index your content.
-
Focus on Mobile Usability:
- Monitor the “Mobile Usability” report to ensure your site is mobile-friendly. Fix issues that may impact mobile user experience.
-
Review Structured Data:
- Check the “Rich Results” and “URL Inspection” reports to validate your structured data (schema markup). Ensure it is correctly implemented for rich search results.
-
Submit and Manage Sitemaps:
- Create and submit XML sitemaps in GSC to help Google understand your site’s structure better. Regularly check for errors and ensure sitemaps are up to date.
-
Monitor Security and Manual Actions:
- Regularly check the “Security & Manual Actions” report in GSC to identify and resolve security issues and manual actions that can affect your SEO.
-
Investigate Page Speed:
- Page loading times can impact SEO. Use GSC’s Core Web Vitals report and other tools to monitor and improve your site’s speed.
-
Set Up Performance Filters:
- Use filters in the “Performance” report to analyze specific queries, pages, countries, or devices. This allows you to target your SEO efforts more effectively.
-
Benchmark and Track Progress:
- Set benchmarks for your key performance metrics and monitor your progress over time. This helps you understand the impact of your SEO efforts.
-
Optimize for Core Web Vitals:
- Google’s Core Web Vitals metrics (LCP, FID, CLS) are now a significant factor in SEO. Use GSC data to identify and fix issues related to these metrics.
-
Stay Informed:
- Regularly read Google’s Webmaster Blog and official guidelines to stay up to date on best practices, algorithm changes, and updates.
-
Act on Insights:
- Use the insights from GSC to make data-driven decisions. Create content, optimize pages, and implement technical changes based on the data you gather.
By effectively utilizing data from Google Search Console in your SEO strategy, you can make informed decisions to improve your website’s visibility in search results and provide a better user experience for your audience. This data-driven approach will help you achieve better SEO results over time.
Best Practices for Ongoing Monitoring and Improvement
Monitoring and improvement are essential for maintaining and enhancing your website’s performance in search engine results. To ensure that your SEO efforts remain effective, consider the following best practices:
-
Regularly Review GSC:
- Continuously monitor GSC to identify and address crawl errors, indexing issues, and performance changes. Pay attention to alerts and notifications from Google.
-
Set Up Automated Reports:
- Create automated reports in GSC to receive regular updates on the performance of your website. This can help you stay informed without manual checks.
-
Track Key Metrics:
- Monitor essential SEO metrics such as clicks, impressions, click-through rate (CTR), average position, Core Web Vitals, and mobile usability on a routine basis.
-
Benchmark Performance:
- Establish performance benchmarks and goals based on historical data. Regularly compare your current performance to these benchmarks to gauge progress.
-
Analyze User Behavior:
- Use Google Analytics in conjunction with GSC to track user behavior, including time on page, bounce rate, and conversion rates. Adjust your content and user experience based on this data.
-
Stay Informed About Algorithm Changes:
- Keep up to date with Google’s algorithm updates and industry best practices. Adjust your SEO strategy as needed to align with the latest trends.
-
Perform Regular Technical Audits:
- Periodically conduct technical SEO audits to check for issues like broken links, slow-loading pages, and mobile usability problems. Address any discovered issues promptly.
-
Optimize content:
- Regularly review and update your website’s content to remain highly relevant. Focus on user intent and optimizing for valuable keywords.
-
Experiment with New Keywords:
- Research and test new keywords to expand your reach and target emerging search trends. Create content around these keywords as part of your ongoing content strategy.
-
Improve User Experience:
- Continuously work on improving the user experience of your website. Ensure it is fast-loading, easy to navigate, and mobile-friendly.
-
Focus on Core Web Vitals:
- Monitor and optimize your website’s Core Web Vitals metrics (LCP, FID, and CLS). Google places increasing importance on these factors.
-
Solicit User Feedback:
- Actively seek feedback from website users and customers. Understanding their needs and addressing their concerns can improve your website’s performance.
-
Regularly Update Structured Data:
- Keep your structured data up to date and ensure it aligns with best practices. This can help you maintain rich results in search listings.
-
Conduct Competitor Analysis:
- Periodically assess the performance and strategies of your competitors in search results. Identify areas where you can outperform them.
-
Set Up A/B Testing:
- Experiment with changes to your website, like different headlines, images, or call-to-action buttons. A/B testing can help you determine what resonates best with your audience.
-
Monitor Social Signals:
- Keep an eye on social media engagement and the impact of social signals on your search performance. High social engagement can indirectly boost your SEO.
-
Seek Expert Opinions:
- Consult SEO experts or agencies to gain fresh perspectives and insights into optimizing your website’s performance.
-
Document and Analyze Results:
- Keep a record of changes you make and the results they achieve. This documentation can help you make informed decisions in the future.
-
Stay Patient and Persistent:
- SEO is an ongoing process, and results may not be immediate. Continue to work on improvements and remain persistent in your efforts.
Implement these best practices for ongoing monitoring and improvement. You can adapt to the changing search landscape and maintain a robust online presence. Regular optimization and staying up to date with SEO trends are essential for long-term success in search engine rankings.
Conclusion: Harness the Power of Google Search Console
In conclusion, GSC is a powerful tool that can be harnessed to enhance your website’s visibility and performance in Google’s search results. Using GSC effectively gives you valuable insights into how Googlebot crawls and indexes your site. You can monitor search performance and address issues that may affect your rankings.
Harnessing the power of Google Search Console is crucial for website owners and webmasters who want to maintain a robust online presence and enhance their SEO efforts. You need to regularly use GSC to monitor, analyze, and optimize your website to improve its visibility, user experience, and overall performance in search engine results.
Recap of the Key Takeaways
Here is a recap of the key takeaways from harnessing the power of Google Search Console.
-
Understand Your Website’s Performance:
Google Search Console provides essential data to understand how your website is performing in Google’s search results. Key metrics include clicks, impressions, click-through rate (CTR), and average position.
-
Resolve Crawl and Indexing Issues:
Regularly monitor GSC for crawl errors, indexing problems, and coverage issues. Addressing these technical issues is crucial for ensuring your website’s content is accessible to search engines.
-
Analyze User Behavior:
GSC offers insights into user behavior. That includes bounce rates, time on page, and conversions. Use this data to refine your content and improve the user experience.
-
Prioritize Mobile Usability:
Review GSC’s Mobile Usability report to ensure your website is mobile-friendly. As mobile usage grows, mobile optimization is crucial for both rankings and user experience.
-
Optimize for Rich Results:
GSC allows you to validate structured data and provides insights into how rich results (rich snippets) are displayed in search results. It enhances your website’s visibility.
-
Maintain Security and Compliance:
Regularly monitor the GSC Security & Manual Actions report to keep your website secure and free from manual actions that can harm your SEO.
-
Focus on Performance Enhancements:
GSC helps you identify opportunities for performance improvements. This addresses page speed issues. It guides you in optimizing for Core Web Vitals and enhances the overall user experience.
-
Refine Your Content Strategy:
Leverage GSC data to refine your content strategy. Identify popular search queries and high-impact pages and create content that aligns with user intent.
-
Ongoing Monitoring and Optimization:
Continuously monitor your website’s performance in GSC, set benchmarks, and act on insights to make data-driven improvements over time.
By harnessing the power of Google Search Console and following these key takeaways, you can enhance your website’s visibility, user experience, and overall performance in search engine results. That will ultimately improve your online presence and SEO efforts.
Encouragement for website owners to make the most of GSC
Dear Website Owners,
You have taken a significant step in your online journey by managing your website. And now, it is time to harness the full potential of GSC. It is not just a tool. It is a gateway to success in the digital realm.
Here is some encouragement to make the most of GSC.
-
Gain Deep Insights:
GSC provides a window into how Google sees your website. You can uncover valuable data about how users find your site. What they do once there, and how your pages perform in search results. Knowledge is power, and GSC is your source of knowledge.
-
Improve Your SEO:
SEO can seem complex, but GSC simplifies the process. It helps you identify technical issues, crawl errors, and indexing problems that may hold your site back. Addressing these issues can boost your website’s rankings and visibility.
-
Enhance User Experience:
With insights into user behavior, you can tailor your website better to meet the needs and expectations of your audience. This translates into happier visitors, more extended visits, and potentially higher conversions.
-
Adapt to Mobile Trends:
Mobile-friendliness is no longer a bonus. It is a necessity. GSC’s Mobile Usability report helps ensure your website looks and works well on mobile devices. It improves your standing in mobile search results.
-
Stand Out with Rich Results:
GSC lets you control your website’s appearance in search results. Implement structured data to enhance your listings with rich snippets. It increases the chances of users clicking on your content.
-
Prioritize Security:
Google Search Console is your ally in maintaining a secure and safe online environment. Regularly check for security issues and manual actions to protect your website’s reputation and search visibility.
-
Boost Page Performance:
GSC points out areas for improvement, from page speed to Core Web Vitals. You can optimize your site’s performance. And you can provide a better experience for users and improve your SEO.
-
Create Valuable Content:
The Performance report shows which search queries lead users to your site. Use this information to shape your content strategy. Do not forget to craft valuable and informative content that aligns with user intent.
-
Embrace Ongoing Optimization:
SEO is not a one-time task. GSC encourages an ongoing optimization mindset. Regularly monitor your site’s performance, set goals, and adapt to stay ahead in the digital landscape.
-
Stay Competitive:
Your competitors are online too. And GSC allows you to keep a watchful eye on their strategies. Use this insight to identify opportunities and surpass your rivals.
Remember, GSC is not just a tool. It is your secret weapon in the online world. It empowers you to make data-driven decisions. That will improve your website’s performance, drive more traffic, and bring success to your online endeavors. So, embrace GSC, explore its features, and shine your website in the digital spotlight. Your journey to online success begins here!
ProDigitalWeb
Additional Resources and References
Official Google Search Console Resources:
Google Search Console Help Center: The official resource for GSC. It offers detailed guides, troubleshooting information, and updates.
The Google Search Console Overview: An overview of GSC’s features and benefits.
The Google Webmaster Central Blog: The official blog for webmasters and SEOs, where Google shares essential updates and insights.
Google Search Console YouTube Channel: Video tutorials and webinars from Google’s own experts on using GSC effectively.
Helpful Articles and Tutorials:
The Ultimate Guide to Google Search Console: An extensive Search Engine Journal guide covering everything from setup to in-depth analysis.
10 Google Search Console Hacks to Boost SEO: A list of tips and tricks to maximize the potential of GSC for your SEO efforts.
How to Use Google Search Console for SEO: A comprehensive guide on utilizing GSC for SEO by SEMrush.
Google Search Console: A Complete Guide: Ahrefs’ guide to Google Search Console covers a wide range of topics and features.
A Guide to Google Search Console: All the Essential Data: A detailed guide on GSC and the essential data it provides.
Google Search Console: The Definitive Guide: Brian Dean’s extensive guide to Google Search Console, complete with actionable tips.
These resources cover a wide range of topics related to Google Search Console. It covers from the basics of setup to advanced usage and SEO strategies. They should help you navigate GSC effectively and improve your website’s performance in Google’s search results.