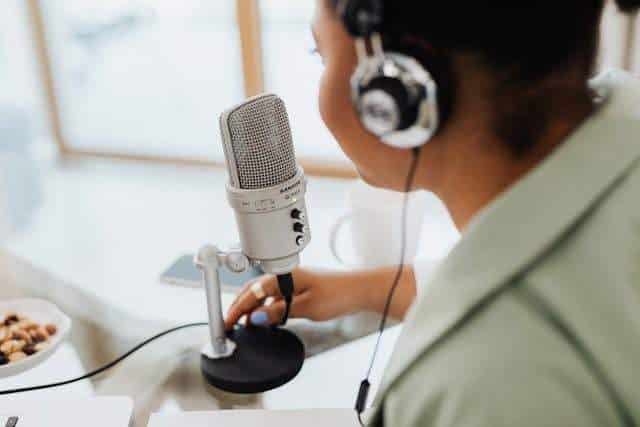
If you are browsing for microphones, you may have found that a few are classified as “tube microphones.” You should know that these microphones come with a vacuum tube. So, compared to other mics, these are different. The vacuum tube is a part of their internal circuitry. People use them to record voices and instruments in the studio. There are a lot of musicians who prefer such types of microphones for their sonic characteristics.
Compared to other microphones, these are a bit more complex. Therefore, these can cost you more. However, multiple tube mics are available at affordable prices. Since the manufacturers started designing solid-state condensers, tube condenser microphones have been considered as less common ones. But this kind of microphones are considered as one of the greatest one till the present date.
What is a Tube Microphone?
A tube microphone is basically an active mic, which is called a large-diaphragm condenser. A vacuum tube is used as its impedance converter. These pass capsule signals via a tube, and thereafter, the signal is outputted. These models are popular for some features, including wide frequency response, quick transient response, capability of capturing detail, and sensitivity to low sound levels.
Usually, internal amplification is used by these mics because of the low audio output from a condenser microphone capsule. Even a few ribbon mics use internal amplification in order to increase the signal level before making the trip through a cable to the mic preamp. Such a type of signal can be noisy without amplification. It can be subject to interference. For amplification, these internal “head amps” are used which can consist of Solid-state circuitry or tube.
Each of these comes with a distinct sonic personality. Tubes can sound “warm”. Besides, these offer a euphonic color to your audio. On the other hand, solid-state amplification can be more neutral. In addition, you can find the solid-state circuitry with a lower noise floor than that of tube circuitry. Compared to a solid-state circuit that is poorly designed, a properly designed tube circuit includes a lower noise floor. You have to know that the first amplification stage takes place inside the mic. If you are willing to raise a condenser mic’s output level, you need to have a microphone preamp up to line level to record audio.
What is a Vacuum Tube?
People know a vacuum tube as a valve or an electron tube. It is an electronic device used to control the flow of current within a vacuum between electrodes if a voltage has been applied. These tubes are made of an outer container that is made of ceramic or glass material. The container comes with a vacuum inside where air is present. Ensure that the tube has no oxygen inside. It prevents the device from burning up.
How Does A Tube Microphone Work?
These microphones come with particular power needs. In the package, a tube microphone has a dedicated power supply as well as a cable. Hence, you need to know that the cable is not the same as a typical XLR mic cable. In the available power supply, it is important to have two audio connectors. The first one is a unique multi-pin connector used to create a connection to the microphone. Another connector uses a standard 3-pin XLR which is used mainly for the audio output.
You need to be more attentive when you set up a tube mic for a recording session than using other mics. Let’s see the method of setting up a tube microphone.
Setup:
- Your first job is to mount this on the mic stand.
- Thereafter, connecting the cable is your job to the power supply from the mic. Suppose you see the cable having a locking collar. Then, ensure that you have not over-tightened it.
- Now, you need to connect your audio input to the mic preamp’s input from the power supply.
- Then, you have to plug in the AC cable of the power supply.
- You should now turn the power supply on. Remember that a few power supplies can get damaged if you turn on them without being connected to a microphone. Some power supplies can be damaged if the mic is “hot plugged.” You can find this disconnected or connected even when the power supply is on.
- It is important to let the mic warm up for 15 to 30 minutes before use. It allows the tube to reach a stable operating temperature. In this way, you can make sure of having a consistent and low noise audio performance.
As soon as the session is completed, you need to follow these steps:
Steps:
- Turning off the power supply is the first task.
- Thereafter, you have to switch off the power supply from the AC outlet.
- The audio output cable and mic cable have to be disconnected now.
- You should thereafter allow your microphone to cool down for at least 15 minutes before moving this or before you store it. Thus protecting the tube is possible from damage because of being jarred when it extends tube life.
- In order to absorb moisture, you have to use a silica gel pack to enclose your microphone in a clean plastic bag. Using the gel, you have to put the mic in its storage case.
What Does A Tube Add To The Sound In A Microphone?
Pushing the head amp can help you to understand the difference between FET and tube. In order to do so, you need to put up the microphone near a sound source.
A tube helps to create extra harmonics, even those that are perceived by the human ear as euphonious. You need to know that it is a fancy word that means ‘nice-sounding.’ The signal compresses gently and sounds mind-blowing.
Why Should You Use A Tube Microphone?
Choosing a microphone for a particular app is just like you are choosing a color from a paint palette. Basically, there are no correct or wrong choices; what matters most is what you want to generate. According to several musicians and engineers, these mics are capable of providing a smooth, warm sound along with a rich low midrange which will be flattering to vocals. Multiple microphones are even designed in that way. However, you can find many tube mics which offer clean and neutral sound.
Vacuum tubes also distort pleasantly. Besides, compared to solid-state amplification devices, these tubes emphasize multiple harmonics. While tubes are used to compress a signal, these are capable of softening transients during the amplification process. These are capable of making a musical sound. Remember that the tube’s sonic behavior relies on the way the circuit designer is working their “voodoo.”
Recording lead vocals is one of its popular applications. Several applications exist where a tube mic is a good option, including drum overheads, acoustic guitar or piano, room mics, chamber ensembles, strings, and woodwinds. You must try a tube mic on a sound source. However, it is not recommended to record the sound of a 24-valve V8 automobile engine with the help of a tube mic.
The Five Parts Of A Tube Microphone:
These mics are made of five important components, including-
- a condenser capsule,
- the vacuum tube,
- a power supply,
- internal circuitry, and
- an output transformer.
Every component has its individual purpose and contributes to the overall sound of the microphone. In order to operate as a complete system, their design was done. Usually, you do not find any matching of them with other components from other mics. When it comes to vintage tube mics of the same brand and model, these can be used with the power supply that is adjusted for use with the tube in that specific model. In most cases, the tube mics come with condenser capsules. But there exist several ribbon mics that are capable of using ribbon elements. Such elements are coupled with internal tube amplification.
-
Condenser Capsule:
The capsule of a condenser microphone, which is a transducer, is the main reason behind the sonic signature of the mic. Besides, this capsule is used to change sound waves into electricity. It includes two metal plates and these are located thousandths of an inch apart. We call one plate the backplate, which remains stationary. Another plate is a thin membrane. It consists of plastic like PVC or Mylar. In order to make the plate conductive, this one is coated with gold’s microscopic layer.
You can move this plate, which serves as a diaphragm. These two plates form a capacitor, which we call a condenser. This electronic component is used to hold an electrical charge. Hence, the voltage that the manufacturer determines needs to be applied to charge or bias the capacitor. Otherwise, the capsule is not going to work.
If the diaphragm remains at rest, the capacitor will hold a specific charge. When there is a change in air pressure, the diaphragm will respond to it. Then, it comes closer to this or goes farther from the backplate. In this way, the amount of charge that it is able to hold is changed. In voltage, this change is called the audio signal.
-
The Role Of Condenser Capsule In Tube Microphones:
Transient response, frequency response and sensitivity are affected by some factors like Diaphragm tension and thickness, size, etc. You should know that condenser mic capsules are not easy to deal with. To design the backplate, brass is used and multiple holes need to be drilled through the plate. Hence, the aim is to tune the frequency response. Also, it targets to generate the pickup pattern you want.
These capsules are capable of creating a fixed pickup pattern. These create different kinds of pickup patterns like omnidirectional, cardioid, and figure-8. Placing two capsules allows you to accomplish it. However, you need to combine the outputs electrically with the varying voltage and phase. A little current is generated by the voltage between the capacitor plates. And the voltage has a high output impedance. As a result, it becomes challenging to connect the capsules to the preamp of your microphone directly. Hence, the internal circuitry of your microphone— mainly the vacuum tube is needed.
-
Vacuum Tube:
It is used to control the current flow. Also this tube amplifies the current flow in an electronic circuit. If this tube works in a microphone, it performs two distinct functions:
-
Functions of Vacuum Tube:
- The first function is that the tube serves as an impedance converter. It helps to decrease the capsule’s output impedance to an impedance that is possible to manage more easily for the remainder of the circuitry of your microphone.
- The second function is that it is used to amplify the audio signal. You should know that the audio signal coming from the capsule is very small. That’s why ensure that the amplification takes place near the capsule. It is the reason the location of the tube is inside the mic.
-
Lifespan Of A Vacuum Tube:
The range of the tubes that are used in the mic is between 12AX7 and the elusive VF14. Ensure that the tubes that have been picked for your mic are tested for low noise levels and low mics. Therefore, if you are thinking that you require any type of replacement, keep in mind that the best source is the manufacturer. They are capable of supplying a tube that you can use in your mic and can give you advice on whether you have to adjust the power supply for the new tube or not.
Remember that the lifespan of vacuum tubes is limited. You can replace them if the existing tube does not work. Besides, it is possible to socket or solder them in place. However, socket and soldering approaches have some differences. You can easily replace the socketed tubes, but these can work loose and are capable of developing noise for oxidation on the contacts.
The soldering approach can deliver you a more reliable connection. But if any replacement is required, you have to go to the manufacturer for help. Or you can go to a microphone tech. But remember that it is not a big problem. The reason is that the tube can last for at least many years based on frequency of use. A few engineers prefer to test with many new swapping brands. They also like to test with New Old Stock (NOS) tubes as they want to change the sound. In addition, they want to change the microphone’s noise floor. If tubes are soldered in place, it isn’t practical.
-
Power Supply:
Tubes need separate low- and high-voltage power supplies. While low-voltage power supplies mean 6V to 12V, high-voltage power supplies mean 100V to 250V. A low-voltage supply is needed for the heater of your vacuum tube. The tube is heated to a certain temperature at which electrons will flow. On the other hand, high voltage will be applied to the anode or plate. It can attract the electron flow. You should know that it is not possible to make such voltages from the 48-volt phantom power in a mic preamp or a mixer. Therefore, ensure that you have an external power supply.
-
More Details About Power Supply:
Power-supply voltages on your mic will be delivered to the same cable that carries the audio. Compared to a generic three-conductor mic cable, a tube-microphone cable is available with more conductors. For tube mics, people use different types of multi-pin connectors. However, later 6- and 7-pin XLR connectors gained popularity of late.
You should know that pins of these connectors are available with small diameters. Besides, these are more fragile than those which are available on a 3-pin XLR. That’s why you must take care to line up the connectors before you insert them into your mic or the power supply. In addition, you should not think that you are capable of swapping cables between tube mics despite having the same connectors. It can happen that different manufacturers use different wiring schemes.
-
On Which Factors Power Supply Depends:
When you use Multi-pattern tube mics, you are capable of finding a pattern-select switch on your mic or power supply. It helps to simplify the internal circuitry of your microphone. Additionally, it includes an option for a recording session. Placing the power supply allows you to change the pattern in the control room when you are willing to hear the result over the control room monitors. If you plan to change the pickup pattern, remember that it could change the amount of room sound captured by your microphone.
If you see the pickup pattern change, you will see a change in the timbre of some multi-pattern mics. Remember that the power supply in the control room relies on the length of the microphone wire. Also, it depends if you are able to sneak the cable through the doorway without causing any damage to it. You can see that the power supply has switches for a high-pass filter or a pad. However, you can find some tube mics where the pad switch is on the mic and the pattern-control switch exists on the power supply.
-
Internal Circuitry:
The tube is a part of the internal circuitry of your mic. It comes with extra stages of amplification, high pass filtering, or a pad. Their purpose is to not prevent the output from overloading the mic preamp when you capture loud sounds. It is also capable of preventing distortion in the mic. If you use a multi-pattern mic, you need to use circuitry in order to switch on the rear diaphragm or switch off this. Also, the circuitry can be used in order to adjust the voltages that are essential to create a change in the pickup pattern. In order to compensate for resonance, the internal circuit is engineered.
-
Output Transformer:
This passive device is used to transfer an audio input to the output without physical contact.
In a tube mic, it is the last stage before audio is transferred to the preamp of your mic. Hence, there are two major purposes of it.
-
Purpose Of Output Transformer:
- The first purpose is to balance the audio signal. It permits the signal to go down long lengths of cable, and you do not need to pick up noise from cell phones, radio stations, or other interference sources.
- Another purpose is to serve as an impedance-matching device that you can see working between the preamp of the mic and tube. Previously, the tube was used as an impedance-matching device. However, the tube’s output impedance is too high to connect this to the mic preamp without creating issues like noise or unnecessary variations in frequency response.
-
The Functions Of Output Transformer
While transformers are useful in solving the above problems, people use them to color the sound. Like tubes, capsules, etc, transformers are also required for the sonic personality of the microphone. When overloaded or saturated, a pleasant type of distortion is generated by them. It is one of the main reasons people prefer using transformers in audio circuits.
A Quick Look At Ribbon Tube Microphones:
When it comes to ribbon tube microphones, you should know that the sound waves hit the ribbon diaphragm. Then, it generates a coinciding audio signal, which is low in level. The voltage of the signal can be increased by a step-up transformer with a high turns ratio. It can help to increase the signal impedance to high levels. Such a signal is fed to the vacuum tube’s grid thereafter. Then, it assists in modulating a higher-quality signal.
Then, the resulting output signal will be sent via the output step-down transformer from the tube to balance properly before the output. Although the transducer element is considered as passive, this microphone will be active. Remember that an internal tube amp is helpful in a low-level microphone type. Thanks to modern technology, because of which the ribbon tube microphones have become so cool.
Factors That Make A Tube Microphone Great:
Each microphone has its individual characteristics. Even tube capsules and circuits come with different characteristics. A few tubes sound “warm” and “smooth.” It is the way we often describe tube microphones. Whereas, we call some tubes sounding “clean” and “bright”, just like the way solid-state condenser microphones are portrayed.
There are a few condenser capsules that can generate reproductions of sound accurately in their audio signals. But others aren’t accurate on that level. Usually, we define tube condenser microphones depending on a few factors. These are warmth, weight, wide frequency response, and compressed sound.
If you want to have a great tube microphone, you first need to decide what kind of sound you need. Also, you must know the applications you are going to use in your microphone. Usually, you can depend on the below-mentioned factors:
- Wide frequency response
- Saturated and compressed (“warm and smooth”) character
- High sensitivity
- Versatility
Wide Frequency Response:
It indicates a wide range of frequencies on which a specific microphone can reproduce in the mic signal. The universal audible frequency spectrum is 20 Hz – 20,000 Hz (cycle/second). It is necessary to have a mic that can recreate a broad range of frequencies if it is not in the range.
The microphone must not overproduce a specific frequency band or underproduce it. Remember that a relatively flat frequency response curve can be critical unless you are after a coloured microphone that accentuates specific brands. A mic that comes with a slight boost or cut in certain frequency ranges will be able to give the mic character. Your microphone does not need to be sensitive in the low-end or high-end. The reason is that we — humans face difficulties in hearing the outskirts of the audible frequency range.
Saturated And Compressed (“Warm And Smooth”) Character:
A compressed and saturated signal is not necessary for a tube condenser microphone. But it can offer the quintessential “tube sound.” You need to calculate the saturation and compressed level. But it depends on how loud the source of sound is in front of the microphone.
It is possible to understand the sound of saturation and compression by the trained ear. Then, you are able to judge whether it is good or bad based on the current situation. Several tube microphones are cherished for the “sound.” If your model has “warm” and “smooth” characters, it will get extra points.
High Sensitivity:
The product you have picked has to be sensitive. Thus, it can help you to pick up sounds with nuance and precision. Additionally, it is able to output a strong audio signal. Its nuanced capture will come from the thin membrane of the capsule. Besides, the strong output can be obtained because of the tube amplifier, which is placed inside the circuitry.
Versatility:
Versatility can make your model much more usable inside & out of the studio. When it comes to talking about a tube condenser, versatility might denote any of the following:
- Multiple switchable polar patterns.
- High-pass filters.
- Passive attenuation devices.
- Alternate circuit paths.
Some Things You Need To Know About Tube Microphone:
Tube Microphones Are Expensive: Tubes, capsules, transformers, and other types of components are not available at cheap prices. If you use inexpensive components, such as capsules, tubes, etc., you have to check the quality. These can affect the mic sound. So, to get the best result, you have to spend more to buy the best tube microphones available in the market.
Tube microphones Are Not Necessarily Better Than FET Microphones: Many people think that compared to tube mics, the quality of solid-state (FET) condensers is less because of the difference in price tag. But that isn’t the case. Like other good and terrible FET mics, there are awesome and terrible tube mics.
Tube Microphones Require Time To Function Properly: FET mics are capable of powering up almost immediately. However sometimes phantom power may need some seconds in order to boot the model up completely. But tube mics take ten minutes or more than that to “warm up” to a consistent sound.
The Bottom Line:
In some specific applications, tube microphones are outstanding. In this article, we have mentioned the top 4 best tube microphones. Pick any of these four according to your budget and requirements.