Introduction to Cloud Computing:
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand accessibility of computing resources as services over the internet. It eliminates the need for businesses to procure, configure, or manage resources. And they only need to pay for what they use.
In other words, Cloud Computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources on the internet with pay-as-you-go pricing. Instead of buying, owning, and maintaining physical data centers and servers, the businesses access technology services, such as computing power, storage, and databases, on an as-needed basis from a provider.
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services, such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics, over the Internet (“The Cloud“). It offers faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. With cloud computing, businesses can access computing resources on demand and only pay for what they use rather than investing in expensive on-premises infrastructure that may go underutilized.
In cloud computing, the cloud service provider takes responsibility for managing and maintaining the computing infrastructure (e.g., servers, storage, networking, operating systems) from the user. The cloud provider typically offers a range of services, such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). These allow businesses to choose the level of control they want over the computing infrastructure.
Thereby it allows businesses to reduce their IT costs. And it increases their agility and focuses on their core business functions rather than managing complex IT infrastructure.
Therefore, Cloud Computing is a model for delivering computing services over the Internet rather than owning and maintaining physical computing resources, such as servers, storage devices, and networking equipment. Businesses can access these resources over the Internet on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Benefits:
Cloud computing is a shift away from traditional IT models where businesses must purchase and maintain their own hardware and software on their premises.It offers businesses several benefits. They are:
- Scalability
- Cost Saving
- Reliability and Availability
- Flexibility
- Security
Scalability:
The cloud computing service is scaled up or down according to the business needs. Businesses can add or remove resources as and when there is a change in demand. It is particularly useful for businesses with fluctuating computing needs. The varying needs may be such as seasonal spikes in demand.
Cost Savings:
Since the businesses only need to pay for the resources they use. Therefore it is more cost-effective than purchasing and maintaining physical infrastructure. Additionally, cloud providers often offer economies of scale that can help reduce costs.
Reliability and Availability:
These computing services are often designed to be highly available and reliable. Many cloud providers offer service-level agreements (SLAs) that guarantee a certain level of uptime.
Flexibility:
Cloud computing services are accessed from anywhere with an Internet connection. These services can enable remote work and collaboration.
Security:
Cloud providers typically offer a wide range of security features, such as firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection. It will help to protect data and applications.
Types of Cloud Computing Services:
There are several types of cloud computing services:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS service model provides businesses with virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking. Businesses can use these resources to build and manage their applications and services.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS model provides businesses with a platform for developing, running, and managing applications. The business needs not to have to manage the underlying infrastructure.
Software as a Service (SaaS): The Software as a Service model provides businesses access to pre-built software applications over the Internet. Businesses can use these applications to manage various functions, such as customer relationship management (CRM), accounting, and human resources.
Types of Deployment Models:
There are also several types of deployment models:
Public cloud: Public cloud is a cloud infrastructure owned and operated by a third-party cloud provider. Multiple businesses can share the same computing resources.
Private cloud: It is a cloud infrastructure dedicated to a single business. The infrastructure is hosted on-premises or by a third-party cloud provider.
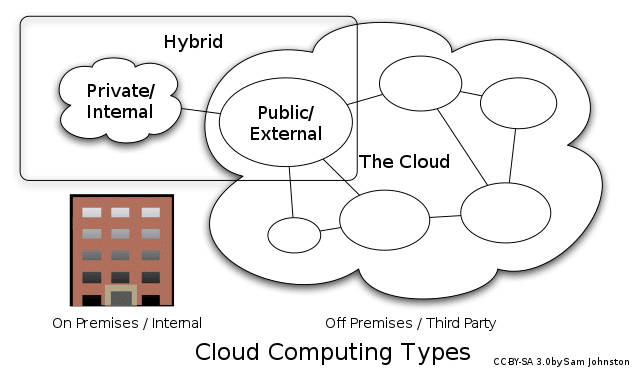
Hybrid cloud: Hybrid is a combination of public and private cloud infrastructures. Businesses can use a hybrid cloud to keep sensitive data in a private cloud. And they use a public cloud for other computing needs.
In general, cloud computing is a model for delivering computing resources over the Internet on a pay-as-you-go basis. It offers businesses several benefits. The benefits are scalability, cost savings, reliability, and flexibility. And there are several types and deployment models for cloud computing, and businesses can choose the model that best meets their needs.
Cloud Computing Definition:
It is a model for delivering computing services over the Internet. It involves accessing on-demand computing resources from a cloud service provider. The resource includes servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics. The resources are accessed and used over the Internet on a pay-as-you-go basis. And it is not being owned and managed by the user. It enables businesses to scale their computing resources up or down as needed. So that it helps to reduce IT costs and allows businesses to focus on their core functions rather than managing complex IT infrastructure. Several types and deployment models for cloud computing include public, private, and hybrid clouds.
Cloud Computing refers to the delivery of computing resources that includes hardware, software, and data storage over the internet or a network of remote servers. Instead of running applications and storing data on a local computer or server, it allows users to access and utilize these resources on-demand, as and when required. It is accessed from anywhere in the world with an internet connection. This technology has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals store, process, and access data and applications. It makes computing more efficient, scalable, and cost-effective.
A Brief History of Cloud Computing:
It has a relatively recent history, dating back to the early 2000s. Here are some key events and milestones in the history of cloud computing:
1999: Salesforce.com introduces the concept of delivering enterprise applications via a simple website.
2002: Amazon Web Services (AWS) launches with a suite of web services to offer online storage and computation.
2006: Amazon launches Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2). It allows users to rent virtual computers to run their own applications.
2008: Google launches its cloud computing platform, Google App Engine. That also enables developers to build and host web applications on Google’s infrastructure.
2009: Microsoft launches Azure, its own cloud computing platform. And Google launches its cloud storage service, Google Cloud Storage.
2010: OpenStack, an open-source cloud computing platform, is launched.
2011: IBM launches its SmartCloud platform. And Oracle launches its cloud offering, Oracle Cloud.
2013: AWS launches its first Virtual Private Cloud service. This service allows customers to create their own isolated cloud environments within AWS.
2016: AWS introduces AWS Lambda, a Serverless computing service that enables developers to run code without provisioning or managing servers.
2018: Microsoft acquires GitHub, a popular platform for hosting and sharing code, and announces plans to integrate it with Azure.
2019: Google launches Anthos, a hybrid and multi-cloud platform that allows customers to manage workloads across different cloud environments.
Since then, cloud computing has continued to evolve and grow. It grows with new technologies and services that are being developed and refined to meet the needs of businesses and individuals worldwide.
Why is cloud computing important?
It has become increasingly important in today’s digital age due to the following reasons:
- Scalability
- Flexibility
- Cost-Effective
- Improved Security
- Increased Efficiency
- Business Continuity
Scalability: Cloud computing models allow businesses to scale their IT resources up or down as and when needed. The business need not have to invest in expensive hardware and software infrastructure.
Flexibility: The users access their applications and data from anywhere, using any device with an internet connection, making it easier to work remotely and collaborate with others.
Cost-Effective: It eliminates the need for businesses to maintain and manage their own IT infrastructure. It will reduce hardware and software costs and eliminate the need for expensive IT staff.
Improved Security: The providers invest heavily in security measures to protect their customers’ data and applications. It provides better security than many organizations that achieve on their own.
Increased Efficiency: It reduces the time and effort required to manage and maintain IT infrastructure. It frees up resources to focus on core business activities.
Business Continuity: Cloud providers offer disaster recovery and business continuity services. That recovery and business continuity ensures that businesses can continue to operate in the event of a natural disaster, cyber-attack, or any other disruptive event. In all, cloud computing has become an essential technology for businesses of all sizes. And it provides a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective way to manage IT resources and drive innovation.
Cloud Computing Models:
Cloud computing offers different models to deliver computing resources over the internet, or a network of remote servers. These models define how cloud services are delivered to the end users. And they have control over the infrastructure.
There are four main cloud computing models:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS),
- Platform as a Service (PaaS),
- Software as a Service (SaaS), and
- Function as a Service (FaaS).
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) IaaS is the basic cloud computing model. It provides customers with virtualized computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking on demand over the internet. With IaaS, customers deploy and manage their applications, data, and services without buying or maintaining their own hardware infrastructure. IaaS providers offer various services, from bare-metal servers to virtual machines to containers. The customer manages and secures the operating system, applications, and data. The best examples of IaaS providers are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and DigitalOcean.
Customers choose the type and size of the infrastructure resources they need and scale up or down as needed. They need not invest in expensive hardware or over-provisioning to accommodate peak demand.
Key Features and Benefits of IaaS:
Scalability: IaaS allows customers to scale their infrastructure resources up or down as needed without investing in expensive hardware or managing capacity planning. Customers can quickly provision additional resources during peak demand and release them when they are no longer needed.
Cost-Effective: It eliminates the need for customers to maintain and manage their own hardware infrastructure. It helps to reduce capital expenditures and operational costs. Customers only pay for the resources they use. There is no need to pay for idle resources.
Flexibility: IaaS allows customers to deploy and manage their applications and services on various operating systems and software stacks. Therefore it gives them greater flexibility and control over their environment. Customers can also choose where to host their infrastructure, depending on their specific requirements for performance, availability, and data sovereignty.
Reliability: IaaS providers offer high levels of redundancy, resilience, and disaster recovery. IaaS ensures that customers’ applications and data are always available, even in the event of a hardware failure, natural disaster, or cyber attack.
Security: Providers invest heavily in security measures, such as network segmentation, access control, encryption, and threat detection. IaaS protects customers’ applications and data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Innovation: It helps the customers to focus on innovation and application development rather than on managing and maintaining their infrastructure. They offer a range of tools and services to help customers automate and optimize their infrastructure and applications, such as monitoring, logging, and analytics.
In all, IaaS is a popular computing model that offers customers a scalable, flexible, and cost-effective way to manage their infrastructure resources. It eliminates the need for customers to manage their own hardware infrastructure. IaaS providers enable businesses to focus on innovation and application development. IaaS also benefits the business with reliability, security, and high availability of cloud computing.
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a computing model. It provides customers a complete platform to develop, deploy, and manage applications. With PaaS, the cloud provider manages the underlying infrastructure, which includes servers, storage, and networking. While the customer focuses on building and running applications. PaaS providers offer a range of development tools, middleware, and runtime environments to help customers build and deploy their applications quickly and easily.
Customers can use it to build, test, deploy, and manage their applications in Platform as a Service (PaaS). PaaS allows for faster time-to-market and greater agility, as well as reduced operational costs. Examples of PaaS providers include Heroku, Google App Engine, and IBM Bluemix.
Key Features and Benefits of Platform as a Service (PaaS):
Productivity:
PaaS eliminates the need for customers to manage the underlying infrastructure. It allows them to focus on developing and delivering their applications faster. PaaS providers offer a range of development tools and services, such as code editors, version control, and continuous integration and deployment. Therefore it helps customers to automate and streamline their application development and deployment processes.
Scalability:
Platform as a Service allows customers to scale their applications up or down as needed. The customer need not worry about the underlying infrastructure. PaaS providers offer various scaling options, such as auto-scaling and load balancing. These options help the customers to handle peak demand and improve application performance and availability.
Cost-Effective:
PaaS eliminates the need for customers to invest in and maintain their own infrastructure. Therefore, it reduces capital expenditures and operational costs. Customers only pay for the platform and services they use without paying for idle resources.
Flexibility:
Platform as a Service enables customers to develop and deploy their applications on various operating systems and software stacks. It gives businesses greater flexibility and control over their environment. Customers can also choose where to host their applications, depending on their specific requirements for performance, availability, and data sovereignty.
Reliability:
This model offers high levels of redundancy, resilience, and disaster recovery. It ensures that customers’ applications are always available, even during a hardware failure, natural disaster, or cyber attack.
Security:
PaaS providers invest heavily in security measures, such as network segmentation, access control, encryption, and threat detection, to protect customers’ applications and data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Innovation:
PaaS model allows customers to focus on innovation and application development rather than managing and maintaining their infrastructure. And, PaaS providers offer a range of tools and services to help customers automate and optimize their application development and deployment processes, such as monitoring, logging, and analytics.
In addition, PaaS is a popular computing model that offers customers a scalable, flexible, and cost-effective way to develop, deploy, and manage their applications. They eliminate the need for customers to manage their own infrastructure. PaaS providers allow businesses to focus on innovation and application development. While it also benefits the business with productivity, scalability, reliability, security, and high availability of cloud computing.
Software as a Service (SaaS):
Software as a Service (SaaS) SaaS is a computing model that delivers software applications over the internet. Customers can use them on demand, usually through a web browser. SaaS providers host and manage the software and the underlying infrastructure, such as servers, storage, and networking. Customers can use the software without installing it on their own devices and pay only for what they use. SaaS applications range from productivity tools like Microsoft Office 365 and Google Workspace to customer relationship management (CRM) software like Salesforce and Hubspot.
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud computing model. Software applications are delivered over the internet, on a subscription basis, to customers. The customers do not have to manage or maintain the underlying hardware and software infrastructure. SaaS providers offer a range of applications, such as email, collaboration, customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), and human resources management (HRM). The customers can access and use the service via a web browser or mobile app.
Key Features and Benefits of SaaS:
Ease of Use:
SaaS applications are easy to use and require minimal installation and setup. Customers can easily access them from any device with an internet connection. They need not install or configure any software.
Scalability:
The applications are scalable and can handle large numbers of users and data volumes. SaaS providers offer various scaling options, such as multi-tenancy and load balancing. This wide range of scaling options enables customers to handle peak demand and improve application performance and availability.
Cost-Effective:
It eliminates the need for customers to invest in and maintain their own hardware and software infrastructure. Thereby it reduces capital expenditures and operational costs. Customers only pay for the software and services they use on a subscription basis. The client need not pay for maintenance, upgrades, or support.
Flexibility:
SaaS applications are customized and configured to meet customers’ specific requirements, such as branding, workflows, and integrations with other software systems. Customers are able to choose from a range of pricing plans and options depending on their specific needs and budget.
Security:
SaaS providers invest heavily in security measures, such as encryption, access control, and threat detection, to protect customers’ data and applications from unauthorized access and cyber threats. SaaS providers also offer high levels of redundancy, resilience, and disaster recovery. This ensures the customers’ applications are always available, even during a hardware failure, natural disaster, or cyber attack.
Innovation:
SaaS providers constantly innovate and add new features and functionality to their applications based on customer feedback and market trends. Customers can benefit from these innovations without investing in their own research and development.
In conclusion, SaaS helps businesses to focus on their core business activities. While it also benefits from the ease of use, scalability, flexibility, security, and innovation of cloud computing.
Function as a Service (FaaS):
Function as a Service (FaaS) FaaS is a cloud computing model. It enables customers to execute code in response to specific events or triggers without managing servers or infrastructure. FaaS providers offer a serverless environment in which customers can upload their code. And the provider will run and scale it automatically in response to incoming requests. FaaS allows for event-driven and highly scalable applications without the need for customers to provision, manage, or scale servers. Examples of FaaS providers are AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, and Microsoft Azure Functions.
Cloud computing models offer different levels of abstraction and control over the infrastructure; they allow the customers to choose the right model for their specific needs. Whether they need raw computing resources, a platform to develop and deploy applications, software applications delivered over the internet, or serverless event-driven architectures. Cloud computing has the right model to fit their requirements.
Function as a Service (FaaS) is a computing model in which customers can execute small units of code, known as functions, in response to specific events or triggers. It helps the developers to write and deploy code without having to manage or provision any infrastructure, such as servers or virtual machines. FaaS is often used in event-driven architectures, such as web applications, chatbots, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Key Features and Benefits of FaaS:
Event-Driven:
FaaS is triggered by specific events or requests, such as a user accessing a web page or an IoT device sending a sensor reading. This enables developers to write code that responds to real-time events rather than having to run continuously in the background.
Scalable:
It automatically scales up or down, based on the number of requests or events, without requiring manual intervention or capacity planning. It helps developers to handle sudden spikes in traffic or demand without having to provide additional infrastructure.
Cost-Effective:
FaaS providers typically charge customers based on the number of requests or events rather than on a fixed infrastructure cost. Therefore the developers need to pay only for the computing resources they actually use rather than having to pay for idle or underutilized capacity.
Developer Productivity:
It allows developers to focus on writing code rather than managing infrastructure or worrying about scalability and availability. It helps developers to be more productive, iterate faster, and deliver code more quickly.
Flexibility:
FaaS supports multiple programming languages and frameworks, allowing developers to choose the tools and technologies that best suit their needs. Providers also offer a range of integration options, such as APIs and webhooks, that enable developers to integrate their functions with other software systems and services.
Easy Deployment:
It enables developers to deploy their code quickly and easily without worrying about server configuration, networking, or security. FaaS providers typically handle these tasks automatically, freeing up developers to focus on writing code.
Some popular FaaS providers are Amazon Web Services (AWS) Lambda, Microsoft Azure Functions, Google Cloud Functions, and IBM Cloud Functions. They offer a range of features and integrations, such as serverless databases, messaging services, and event hubs. It enables developers to build complex and scalable applications using FaaS.
In conclusion, function as a Service (FaaS) is a powerful computing model that enables developers to write and deploy code quickly and easily without having to manage any infrastructure. FaaS offers various features and benefits, including event-driven architecture, scalability, cost-effectiveness, developer productivity, flexibility, and easy deployment. FaaS is well-suited for event-driven architectures, web applications, chatbots, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. And it is becoming an increasingly popular choice for cloud-native application development.
The Benefits and Drawbacks of Cloud Models:
Benefits and Drawbacks of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
Benefits:
High scalability and flexibility, allowing organizations to adjust their infrastructure according to their needs
Cost-effective, as organizations only pay for the resources they use
Minimum need for maintenance and hardware management, as the cloud provider handles these tasks
Reduced upfront costs, as organizations do not need to purchase and maintain their own hardware and infrastructure
Drawbacks:
Requires significant technical expertise and knowledge to manage the infrastructure effectively
As organizations are responsible for securing their applications, it raises more data Security concerns.
Very limited customization and control over the infrastructure
Benefits and Drawbacks of Platform as a Service (PaaS):
Benefits:
Easier and faster application development (The platform provides a pre-configured environment and tools for development)
Less need for hardware and software management (the platform provider handles these tasks)
Improved scalability and flexibility, allowing organizations to focus on their applications rather than infrastructure management
Drawbacks:
Limited customization options, as the platform provider may restrict access to certain features or tools, may not be suitable for all types of applications, as the platform may not support certain programming languages or technologies.
Potential lock-in to a particular platform, which may limit flexibility in the long term
Benefits and Drawbacks of Software as a Service (SaaS):
Benefits:
Since the organizations only pay for the software they are using, it reduces upfront costs and lowers the total cost of ownership. The software is provided and managed by the cloud provider; therefore, it has faster deployment and easier maintenance. SaaS allows organizations to adjust their software usage according to their needs; therefore, the scalability and flexibility are high.
Drawbacks:
Limited customization options (organizations may not be able to modify the software to meet their specific needs).
As the cloud provider is responsible for securing the data and applications, Security concerns are very high.
Potential data portability issues (organizations may not be able to easily move their data to another provider or platform)
Benefits and Drawbacks of Function as a Service (FaaS):
Benefits:
Reduced costs (Organizations only need to pay for the computing resources they use for their specific functions)
Increased agility (organizations are allowed to deploy and scale specific functions in response to the changing demand quickly and easily)
Reduced maintenance and management overheads (The cloud provider handles the infrastructure management tasks)
Drawbacks:
Limited customization options (The functions are pre-defined and may not meet all of an organization’s specific needs)
Potential performance issues (The functions may not be optimized for certain workloads or use cases)
Security concerns (Organizations are responsible for securing their own applications and data)
Every cloud computing model has its own set of benefits and drawbacks, and organizations should carefully evaluate their computing needs and requirements before choosing a model. Factors to consider atechnical expertise, customization options, security requirements, scalability needs, and cost considerations.
Cloud Deployment Models:
Cloud deployment models refer to the different ways in which computing resources are provisioned and managed. There are three primary deployment models, and they are public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud.
Public Cloud:
A public cloud is a computing environment that is open to the general public. And it is hosted by a third-party cloud provider. Public clouds are typically accessible via the internet and used by anyone with an account with the provider. In addition, Public clouds offer a wide range of computing services, including computing, storage, networking, databases, and analytics. They are scalable, flexible, and cost-effective. But, it may have security and compliance concerns.
Key Features and Benefits of Public Clouds:
Scalability:
Public clouds can quickly scale up or down to meet the changing demands of applications or services without any manual intervention. It means that organizations can easily increase or decrease their computing resources, depending on their specific needs. Organizations need not invest in additional hardware or infrastructure.
Cost-effectiveness:
Public clouds offer a pay-as-you-go pricing model. It means customers only pay for the computing resources they actually use. It is especially beneficial for small and medium-sized businesses. Therefore, small and medium-sized businesses can avoid the high upfront costs of purchasing and maintaining their IT infrastructure.
Accessibility:
It can be accessed from anywhere in the world with an internet connection. This means; that organizations can easily collaborate with partners, customers, and employees, regardless of location.
Wide range of services:
Besides, it offers a wide range of services that includes computing, storage, networking, databases, and analytics, among others. Organizations can easily choose the services that best meet their specific needs without having to invest in additional hardware or infrastructure.
High reliability:
Public clouds are typically designed to provide high availability and reliability, with multiple layers of redundancy and failover mechanisms. So that businesses can ensure that their applications and services are always up and running, even in the event of hardware failures or other disruptions.
Some of the most popular public cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These providers offer a wide range of services that includes virtual machines, storage, databases, analytics, machine learning, and serverless computing. Public cloud providers also offer a range of tools and services to help organizations manage and optimize their cloud resources that includes monitoring, automation, and security.
However, there are also some potential drawbacks to using public clouds. One concern is security and compliance. As public clouds are shared by multiple users and may be vulnerable to cyberattacks. In addition, public clouds may not be suitable for all applications and workloads. Especially that requires high levels of customization or control.
Though, public clouds offer a range of benefits that includes scalability, cost-effectiveness, accessibility, a wide range of services, and high reliability. Organizations should carefully evaluate their computing needs and requirements. And they need to choose a public cloud provider who best meets their specific needs while ensuring security and compliance.
Private Cloud:
A private cloud is a cloud computing environment that is dedicated to a single organization or user group. Unlike public clouds, private clouds are not open to the general public.
They are typically hosted on-premises or in a data center that is owned and operated by the organization. Private clouds are managed by the organization’s IT department or by a third-party service provider. Private clouds offer greater control and security.
It enables organizations to have greater control over their computing resources that, includes hardware and software. But Private clouds are more expensive and less scalable than public clouds. Since all computing resources are dedicated to a single organization, they can provide greater reliability and uptime.
Key Features and Benefits of Private Clouds:
Some of the key features and benefits of Private Clouds:
Security and Control:
Private clouds offer a higher level of security and control compared to public clouds. The computing resources are dedicated to a single organization or user group. It means that organizations can implement their own security policies and procedures. And it can ensure that their data and applications are not accessible to unauthorized users.
Customization:
The organizations have full control over the hardware, software, and networking infrastructure in the private cloud. Therefore, it offers a higher degree of customization compared to public clouds. That means that organizations can tailor their cloud environment to meet their specific needs and requirements. And they can optimize the performance and cost-effectiveness of their cloud resources.
Compliance:
Private clouds are often used by organizations that operate in highly regulated industries, such as healthcare, finance, or government. It offers a higher level of compliance compared to public clouds. Since all computing resources are isolated from the public internet, it offers enhanced security and compliance. As organizations can ensure that their data and applications are stored and processed in accordance with industry-specific regulations and standards.
Cost-effectiveness:
Private clouds are more cost-effective compared to public clouds, especially for organizations that have a steady demand for computing resources. It is because private clouds are optimized for specific workloads. And the organizations can avoid the costs associated with over-provisioning or underutilization of computing resources.
Reliability:
It can offer high reliability and uptime, as organizations can implement their own failover mechanisms and disaster recovery procedures. It ensures that the organization’s applications and services are always available, even during hardware failures or other disruptions.
Some of the popular private cloud solutions include VMware, OpenStack, and Microsoft Azure Stack. These solutions offer a wide range of features and tools to help organizations. These tools and features help organizations to manage and optimize their private cloud resources that include virtualization, orchestration, automation, and monitoring.
However, there are also some potential drawbacks to using private clouds. One concern is the high upfront costs associated with building and maintaining private cloud infrastructure. In addition, private clouds may not offer the same level of scalability and flexibility compared to public clouds. Especially for organizations with unpredictable or fluctuating demands for computing resources, the private cloud could not provide scalability and flexibility as expected.
Organizations should carefully evaluate their computing needs and requirements. And then choose a private cloud solution that best meets their specific needs. In addition, they need to ensure that cost and scalability concerns are addressed.
Hybrid Cloud:
A hybrid cloud is a cloud computing environment that combines the use of public and private cloud services. It allows organizations to leverage the benefits of both cloud deployment models. In a hybrid cloud, the public and private cloud environments are connected through a highly secured network connection to allow seamless data and application integration. It offers the best of both private and public clouds. It provides the scalability and flexibility of public clouds, along with the security and control of private clouds.
Key Features and Benefits of Hybrid Cloud:
Flexibility:
Hybrid clouds offer a high degree of flexibility. Organizations can choose to host their data and applications in either the public or private cloud, depending on their specific needs and requirements. It allows organizations to optimize their cloud resources for different workloads. It helps organizations balance their workloads, optimize costs, and ensure data security and compliance. Further, it also ensures that the organizations have access to the resources when they need.
Scalability:
Hybrid clouds offer a high level of scalability. Organizations can dynamically provision and de-provision computing resources in response to changes in demand. This means that organizations can quickly and easily scale their computing resources up or down, depending on the workload, without incurring significant costs.
Cost-Effectiveness:
It is more cost-effective compared to using a single cloud deployment model. Organizations can leverage the cost advantages of public clouds for non-sensitive workloads. At the same time, they can also maintain control and security over sensitive data and applications in the private cloud. Therefore organizations can optimize their cloud spending while ensuring the level of security and control that they need.
Security:
Hybrid clouds offer a high level of security. Businesses can ensure that sensitive data and applications are stored and processed in the private cloud. And the non-sensitive workloads are hosted in the public cloud. This means; that organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches and other security threats. And it also ensures that they are compliant with industry-specific regulations and standards.
Disaster recovery:
Hybrid providers offer a high level of disaster recovery. Organizations can replicate their data and applications across both public and private cloud environments. In the event of a disaster or outage, organizations can quickly and easily recover their data and applications without incurring significant downtime or data loss.
Some of the popular hybrid cloud solutions include Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud Platform. These solutions offer a range of features and tools to help organizations manage and optimize their hybrid cloud resources. Their service includes virtualization, automation, and monitoring.
However, there are also some potential challenges to using hybrid clouds. One concern is the complexity of managing and integrating public and private cloud environments. It requires specialized skills and expertise to manage and integrate both private and public clouds. In addition, hybrid clouds require additional network bandwidth and infrastructure. That will increase the overall cost of the cloud environment.
Overall, hybrid clouds offer a range of benefits that includes flexibility, scalability, cost-effectiveness, security, and disaster recovery. Organizations should carefully evaluate their computing needs and requirements. And then choose a hybrid cloud solution that best meets their specific needs. In addition, they should also ensure that cost, complexity, and scalability concerns are addressed.
Community Cloud:
A community cloud is a cloud deployment model that is shared among multiple organizations. They have similar interests and concerns, such as compliance requirements or regulatory constraints. In a community cloud, the participating organizations share the same infrastructure, resources, and services. And they maintain a high level of privacy, security, and control over their data and applications.
Community clouds are typically managed and operated by a third-party cloud service provider.
The service provider is responsible for ensuring that the cloud environment meets the specific needs and requirements of the participating organizations. The cloud service provider may also provide additional services and tools, such as monitoring, management, and support, to help the participating organizations optimize their cloud resources. And they ensure that their data and applications are secure and compliant.
Key Features and Benefits of Community Cloud:
Collaboration:
Community clouds offer a high degree of collaboration. All the participating organizations can work together to leverage their shared resources and services. Since the organizations can share knowledge, expertise, and best practices, the community cloud will be improved in efficiency, reduced costs, and increased innovation.
Compliance:
Community clouds are often used by organizations that have similar compliance requirements, such as healthcare providers, financial institutions, or government agencies. By sharing the same cloud environment, these organizations can ensure that their data and applications are compliant with regulatory requirements without incurring significant costs or complexity.
Control:
The participating organizations can maintain a high level of privacy, security, and control over their data and applications. Therefore the Community clouds offer a high degree of control. It means that they can customize their cloud resources to meet their specific needs and requirements without compromising security or compliance.
Cost-Effectiveness:
The organizations are sharing the cost of the infrastructure, resources, and services. Therefore, Community clouds are more cost-effective than a single cloud deployment model. It means that they can optimize their cloud spending. And also ensure that they have access to the resources they need when they need them.
Scalability:
Organizations can dynamically provision and de-provision computing resources in response to changes in demand. Therefore Community clouds can offer a high level of scalability. Depending on the workload, they can quickly and easily scale their computing resources up or down without incurring significant costs.
Some examples of community cloud solutions include the Amazon GovCloud, designed specifically for government agencies and contractors. The Google Cloud Government Community Cloud is designed for government agencies and organizations that require compliance with specific security standards.
Community clouds offer various benefits, including collaboration, compliance, control, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. Organizations should carefully evaluate their computing needs and requirements. They need to choose a community cloud solution that best meets their specific needs while ensuring that privacy, security, and compliance concerns are addressed.
Key Features and Components of Cloud Computing
Key Features:
On-Demand Self-Service: Cloud computing allows users to access computing resources on-demand without human intervention. Users can provision and de-provision resources, such as virtual machines or storage, if needed, quickly and easily.
Broad Network Access: Using a variety of devices such as laptops, Smartphones, or tablets, users can access computing resources from anywhere. This is made possible through the use of web-based interfaces or APIs.
Resource Pooling: It allows multiple users to share a pool of computing resources, such as servers, storage, or networks. Resources are dynamically allocated based on changing demands. This feature enables greater efficiency and flexibility in resource allocation.
Rapid Elasticity: Cloud computing enables computing resources to be rapidly scaled up or down in response to changing demands. This feature allows organizations to quickly respond to spikes in traffic or workload demands without investing in additional hardware or infrastructure.
Measured Service: Cloud computing allows users to monitor and track their resource usage. It enables the user to accurately predict and manage costs. Besides, user can optimize their resource allocation based on actual usage. It allows users to pay for the resources they use.
Components:
In addition to these key features, cloud computing is composed of several components that enable the delivery of these features. These components are:
- Virtualization
- Service models
- Deployment models
- Cloud providers
Virtualization: Cloud computing relies heavily on virtualization technology. It enables multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical machine. It offers greater efficiency and flexibility in resource allocation. Further, it offers improved security and isolation between different virtual machines.
Service Models: Cloud computing offers several different service models, such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), and Function as a Service (FaaS). Each service model provides different levels of abstraction and management for computing resources.
Deployment Models: Cloud computing offers several different deployment models. They are public, private, hybrid, and community clouds. Each deployment model provides different levels of control and security over the computing resources.
Cloud Providers: Cloud computing is delivered by various cloud providers. A few of them are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and many others. These cloud providers offer different levels of functionality, pricing, and support, allowing organizations to choose the provider that best fits their needs.
It offers many key features and components that enable organizations to access computing resources quickly, easily, and efficiently. Organizations can optimize their computing infrastructure by leveraging virtualization technology, service models, deployment models, and cloud providers. So that it will reduce costs while improving scalability and flexibility.
Virtualization:
Virtualization is a foundational technology that underpins cloud computing. It enables multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical machine, allowing for greater efficiency and flexibility in resource allocation. Virtualization allows organizations to abstract their computing resources from their physical hardware, such as servers, storage, and networking. Cloud computing creates virtual versions of these resources that are used independently and dynamically.
There are several types of virtualization, such as:
- Server virtualization
- Storage virtualization
- Network virtualization
Server virtualization: Server virtualization is the most common type of virtualization. And it involves running multiple virtual machines on a single physical server. Each virtual machine operates as if it were a separate physical server. Each virtual machine operates with its own operating system and applications.
Storage virtualization: Storage virtualization involves creating a virtual layer on top of physical storage devices. It allows them to be managed as a single pool of storage. It enables more efficient use of storage resources. And Storage virtualization improves flexibility in allocating storage to different applications and users.
Network Virtualization: Network virtualization involves creating virtual networks on top of physical networks. It allows them to be managed as a single network. Network virtualization enables greater flexibility in network configuration and management. And Network virtualization allows for better isolation and security between different virtual networks.
The Benefits of Virtualization:
Improved Efficiency: Virtualization enables organizations to use their computing resources more efficiently by consolidating multiple virtual machines onto a single physical server. Virtualization reduces the amount of hardware needed to support their applications.
Better Resource Utilization: Virtualization allows organizations to allocate computing resources more effectively. Which virtualization, the user can use their hardware more effectively and reduce costs associated with over-provisioning.
Increased Agility: Virtualization helps organizations to quickly provision and de-provision resources as needed. It means that they can respond to changing business needs more quickly and efficiently.
Improved Disaster Recovery: With Virtualization, organizations can create virtual copies of their computing resources. And they can quickly recover from disasters and reduce downtime associated with data loss or system failures.
Drawbacks of Virtualization:
Despite its many benefits, virtualization also has some drawbacks.
Complexity: For organizations that are new to the technology, virtualization is complex to set up and manage. It can lead to increased costs and challenges in maintaining virtualized environments.
Performance Overhead: Virtualization can add some performance overhead, particularly for applications that require high levels of processing power or input/output (I/O) operations.
Security Concerns: Virtualization can introduce new security risks. If virtual machines are not properly isolated from each other, or if there are vulnerabilities in the virtualization software, it will lead to security issues.
Virtualization is a critical technology that enables cloud computing and provides many benefits for organizations looking to optimize their computing infrastructure. Though there are some drawbacks associated with virtualization, it has many benefits. These benefits make it a powerful tool for improving efficiency, resource utilization, agility, and disaster recovery.
Scalability:
Scalability refers to the ability of a system to handle increasing levels of work or growth without compromising performance, reliability, or quality of service. In cloud computing, scalability is critical in ensuring that applications can adapt to changing workloads and user demands.
There are two types of scalability:
Vertical Scalability: Vertical scalability, also known as scale-up, refers to increasing the capacity of an individual server or virtual machine. It is increased by adding more RAM, increasing processing power, or expanding storage capacity.
Horizontal Scalability: Horizontal scalability, also known as scale-out, refers to adding more resources to a system by adding more servers or virtual machines. It allows the application to distribute workloads across multiple resources, improving performance and availability.
The Benefits of Scalability:
Cost Savings: Scalability allows organizations to optimize resource usage. It can result in cost savings by reducing the need for over-provisioning and minimizing wasted resources.
Improved Performance: Scalability improves the performance of applications. It enables them to handle increasing workloads and user demands without experiencing bottlenecks or slowdowns.
Increased Reliability: It also increases the reliability of applications by reducing the risk of downtime due to unexpected spikes in demand or resource constraints.
Enhanced User Experience: Scalability improves the user experience. Scalability ensures that applications are responsive and available at all times, even during periods of high demand.
The Challenges of Scalability:
Despite its many benefits, scalability also has some challenges. They are:
Complexity: Scalability is complex to implement and manage. It is particularly for organizations that are new to cloud computing or have limited resources.
Cost: Scalability is expensive, particularly if an organization needs to add more resources to accommodate increasing demand.
Technical Limitations: There may be technical limitations to scalability. It is particularly for applications that require high levels of processing power, memory, or storage.
Scalability is a critical factor in cloud computing that enables organizations to adapt to changing workloads and user demands. While scalability has many benefits, it also poses challenges that include complexity, cost, and technical limitations. To achieve scalability, organizations need to carefully plan and manage their resources to ensure that they can effectively handle increasing demand and maintain the performance, reliability, and quality of service of their applications.
Elasticity:
Elasticity is a key feature of cloud computing. It allows resources to be dynamically provisioned and de-provisioned to meet changing workloads and user demands. Elasticity enables cloud computing to scale resources up and down as and when needed. It ensures that applications have the right level of resources to meet their performance and availability requirements.
Elasticity is different from scalability. It involves the automatic provisioning and de-provisioning of resources based on real-time demand. Elasticity means that resources are added or removed in response to changes in workload without human intervention. It allows computing environments to respond quickly and effectively to changing demands.
The Benefits of Elasticity:
Improved Resource Utilization: Elasticity allows organizations to optimize resource usage. It results in cost savings by reducing the need for over-provisioning and minimizing wasted resources.
Improved Performance: Elasticity improves the performance of applications by ensuring that they have the right level of resources to meet changing demands. It prevents bottlenecks and slowdowns, even during periods of high demand.
Increased Reliability: Elasticity increases the reliability of applications by ensuring that resources are available when they are needed. It reduces the risk of downtime and ensures that applications are always responsive and available.
Enhanced User Experience: Elasticity improves the user experience by ensuring that applications are responsive and available at all times, even during periods of high demand. It helps to increase user satisfaction and loyalty.
The Challenges of Elasticity:
Despite its many benefits, elasticity also has some challenges.
Complexity: Elasticity is complex to implement and manage, particularly for organizations that are new to cloud computing or have limited resources.
Cost: Elasticity is expensive, particularly if an organization needs to add more resources to accommodate increasing demand.
Technical Limitations: There may be technical limitations to elasticity. It is particularly for applications requiring high levels of processing power, memory, or storage.
Elasticity is a critical feature of cloud computing that enables resources to be dynamically provisioned and de-provisioned to meet changing workloads and user demands. Though elasticity has many benefits, it also poses challenges that include complexity, cost, and technical limitations. To achieve elasticity, organizations need to carefully plan and manage their resources. The resource needs to effectively handle changing demand and maintain the performance, reliability, and quality of service of their applications.
Multitenancy:
Multitenancy is a key feature of cloud computing that allows multiple customers or tenants to share the same computing resources that, include servers, storage, and networking infrastructure. It means that different customers can use the same application or service while their data and computing resources are kept separate and secure.
The Benefits of Multitenancy
Multitenancy offers a number of benefits to cloud service providers and their customers.
Cost Savings: Multitenancy helps to reduce costs by enabling cloud providers to share computing resources among multiple customers. It reduces the need for over-provisioning. And it minimizes the number of unused resources.
Scalability: It enables cloud providers to scale their resources up and down in response to changing demand. It ensures that they have the right level of resources to meet their customers’ needs.
Customization: Multitenancy allows cloud providers to offer customized services to different customers based on their unique needs and requirements.
Security: It provides a secure environment for different customers. It ensures that their data and computing resources are kept separate and secure.
The Challenges of Multitenancy
However, Multitenancy also poses some challenges and risks.
Data privacy: Multitenancy requires careful management of data privacy and security to ensure that each customer’s data is kept separate and secure.
Performance: It impacts performance, particularly during periods of high demand, if resources are not adequately provisioned or shared.
Customization
Limitations: Multitenancy can limit the level of customization that cloud providers can offer to their customers. A provider needs to balance the needs of different tenants to maintain a consistent and secure environment.
To overcome these challenges, cloud providers need to implement strong security and data management practices, and they need to ensure that their resources are adequately provisioned and shared among their customers. They also need to provide effective tools and services to help their customers to manage their applications and services in a multitenant environment. Overall, Multitenancy is a powerful feature of cloud computing that enables cost-effective and flexible sharing of resources among multiple customers. But it requires careful planning and management to ensure its benefits are realized while minimizing its risks.
High Availability:
High Availability (HA) is a critical requirement for many cloud computing applications and services. It refers to the ability of a system or application to remain available and functioning even in the event of hardware or software failures, network outages, or other disruptions. High Availability is achieved through a combination of redundancy, fault tolerance, and failover mechanisms.
Key features of High Availability:
There are several key features and components of High Availability in cloud computing, including:
Redundancy: Redundancy refers to the use of multiple components, such as servers, storage devices, and network connections. It ensures that if one component fails, the system or application can still function using the remaining components. Redundancy is achieved through hardware duplication, such as using multiple servers, or through software replication, such as using virtualization technologies to replicate servers or applications.
Fault tolerance: Fault tolerance is the ability of a system or application to continue functioning even in the presence of faults or errors, such as hardware failures or software bugs. Fault Tolerance is achieved through various mechanisms, such as error detection and correction, data backup and recovery, and automated failover.
Failover: Failover is the process of automatically transferring control and workload from a failed component to a backup component to maintain availability and performance. Failover mechanisms are implemented at various levels, such as network routing, load balancing, or application failover.
Load Balancing: Load Balancing is the distribution of workloads across multiple servers or instances. In order to optimize resource utilization and ensure High Availability, Load Balancing is crucial. Load Balancing is implemented through various mechanisms, such as round-robin DNS, hardware load balancers, or software load balancers.
Benefits of High Availability:
High Availability offers several benefits for cloud computing applications and services, including:
Improved Uptime: High availability ensures that applications and services remain available even during hardware or software failures, network outages, or other disruptions. It helps to improve uptime and reduce downtime.
Enhanced Performance: High availability enables applications and services to scale dynamically based on demand. It ensures that they can deliver optimal performance and responsiveness.
Increased Reliability: High availability provides a level of reliability and redundancy. It ensures that applications and services are always available. And it can deliver consistent and predictable results.
Limitations and Challenges of High Availability:
However, high availability also has some limitations and challenges.
Increased Complexity: High Availability requires additional hardware, software, and networking components. These components can increase the system’s complexity and make it more difficult to manage.
Higher Costs: It also requires additional hardware, software, and networking components investments. Therefore it can increase the costs of deploying and maintaining cloud computing applications and services.
Configuration and Maintenance: High Availability requires careful configuration and ongoing maintenance to ensure that all components work properly. And it tests the failover mechanisms and updates them regularly.
Therefore, High Availability is a critical feature of cloud computing that can help to ensure that applications and services are always available, responsive, and reliable. However, it requires careful planning, management, and investment to achieve its benefits while minimizing its risks and limitations.
Disaster Recovery:
Disaster Recovery is a critical component of cloud computing that refers to the process of restoring operations and data in the event of a major disruption or disaster, such as a natural disaster, cyber attack, or hardware failure. The goal of disaster recovery is to minimize downtime and data loss. And it ensures that business operations are resumed as quickly as possible.
Key Features and Components of Disaster Recovery:
There are several key features and components of disaster recovery in cloud computing.
Backup and Recovery: Backup and Recovery is the process of creating and maintaining copies of critical data and applications and restoring them during a disruption or disaster. Backup and recovery are achieved through various mechanisms, such as regular data backups, replication to remote locations, or real-time synchronization.
Disaster Recovery Plan: A disaster recovery plan is a comprehensive strategy that outlines the steps and procedures to be followed in the event of a major disruption or disaster. The plan should include:
- A detailed inventory of critical systems and data.
- A list of priority tasks and personnel.
- Clear instructions for restoring operations.
Redundancy and Failover: Redundancy and failover refer to the use of multiple components, such as servers, storage devices, and network connections, to ensure that if one component fails, the system or application can still function using the remaining components. Redundancy and failover are achieved through hardware duplication, using multiple servers, or through software replication, using virtualization technologies to replicate servers or applications.
Disaster Recovery Testing: Disaster recovery testing is the process of simulating a disaster or disruption to test the effectiveness of the disaster recovery plan and procedures. Testing should be conducted regularly to ensure that the plan is up-to-date and effective and to identify any areas that require improvement.
Benefits of Disaster Recovery:
Disaster Recovery offers several benefits for cloud computing applications and services.
Improved Business Continuity: Disaster Recovery ensures that critical systems and data are protected and can be restored quickly during a major disruption or disaster. It helps to improve business continuity and minimize downtime and data loss.
Enhanced Security: Disaster Recovery also helps to enhance security by providing multiple layers of protection and redundancy. It reduces the risk of data loss or theft. It ensures that critical systems and data are always available and secure.
Compliance: Disaster Recovery is often required by industry regulations and standards, such as HIPAA or PCI DSS. And it helps organizations to comply with these requirements.
Disaster Recovery Limitations and Challenges:
However, disaster recovery also has some limitations and challenges.
Cost: Disaster Recovery is more expensive, as it requires additional investments in hardware, software, networking components, and ongoing testing and maintenance.
Complexity: It requires careful planning and coordination. It is complex to implement and manage. It requires expertise in areas such as data backup and recovery, networking, and security.
Scalability: Disaster Recovery is difficult to scale if the volume of data and complexity of systems increases. Organizations must carefully plan and design their Disaster Recovery strategy to ensure that it can accommodate future growth and changes.
Overall, disaster recovery is a critical component of cloud computing that can help to ensure that business operations are protected. And it can be restored quickly in the event of a major disruption or disaster. However, it requires careful planning, investment, and ongoing maintenance to ensure that it is effective and meets the organization’s needs.
Cloud Computing Architecture
Cloud computing architecture refers to the structure of a computing system. Architecture is made up of various components and layers that work together to provide cloud services to users. The architecture is designed to provide a highly scalable, reliable, and secure infrastructure supporting a wide range of applications and workloads.
There are typically three main layers in cloud computing architecture:
Infrastructure Layer:
The infrastructure layer provides the physical and virtual resources needed to support cloud services. This layer includes servers, storage devices, network devices, and other hardware and software components used to create the cloud infrastructure.
Platform Layer:
The platform layer provides a set of tools and services that are used to build, deploy, and manage cloud applications and services. It includes operating systems, middleware, databases, and other tools and services used to develop and run cloud applications.
Application Layer:
The application layer is where cloud applications and services are hosted and provided to users. It is the actual applications and services accessed by users, such as email, online storage, and web applications.
Within these layers, there are various components that makeup cloud computing architecture, including:
Virtualization:
Virtualization is a key component of cloud computing architecture that allows multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical machine. It optimizes resource usage and increases efficiency. And also it enables faster and more flexible deployment of applications.
APIs:
APIs, or application programming interfaces, are used to facilitate communication between different components of the cloud infrastructure. And, APIs enable developers to access and manipulate cloud resources, such as virtual machines and storage, and integrate them into their applications.
Load Balancers:
Load Balancers distribute network traffic across multiple servers or resources to ensure that applications remain highly available and responsive, even during periods of high demand.
Security:
Security is a critical component of cloud computing architecture. It ensures that data and applications are protected from unauthorized access and attacks. It includes firewalls, encryption, access controls, and monitoring.
Cloud computing architecture is designed in different ways, depending on the specific needs and requirements of the organization. For example, some organizations may opt for a public cloud architecture, while others may prefer a private or hybrid cloud architecture. Regardless of the specific architecture used, designing and implementing a secure, scalable, and reliable cloud infrastructure that can support the organization’s business needs and goals is essential.
Cloud Computing Architecture Types:
There are four main types of cloud computing architecture:
Public Cloud Architecture:
Public cloud architecture is the most common type of cloud architecture, where cloud resources and services are made available to the general public over the internet. These resources are provided and managed by third-party cloud service providers, who maintain and operate the infrastructure on behalf of the users. Public cloud architecture is characterized by its scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. The users can easily scale up or down their resources as needed and only pay for what they use.
Private Cloud Architecture:
Private cloud architecture is designed for use by a single organization or company. And the infrastructure is owned, managed, and operated by that organization. Private cloud architecture provides greater control and customization than public cloud architecture. A private cloud is ideal for organizations that require strict security and compliance measures.
Hybrid Cloud Architecture:
Hybrid cloud architecture is a combination of public and private cloud architectures. In Hybrid, some resources and services are provided by a third-party cloud service provider, while others are owned and managed by the organization. The hybrid architecture enables organizations to leverage the benefits of both public and private cloud architectures. The businesses can balance their workload between the two environments.
Multi-Cloud Architecture:
Multi-cloud architecture is a type of cloud architecture that involves the use of multiple cloud service providers to host and manage different aspects of an organization’s IT infrastructure. This architecture provides greater redundancy and resiliency than other cloud architectures. And it helps organizations avoid vendor lock-in.
In addition to these four main types of architecture, there are also various cloud deployment models, such as Community Cloud and Distributed Cloud, which are used to meet specific business needs and requirements. Ultimately, the choice of architecture and deployment model will depend on various factors. It includes an organization’s business goals, IT requirements, security and compliance needs, and budget.
Front-End and Back-End Architecture:
Front-end and back-end architectures are two distinct components of cloud computing architecture that work together to deliver applications and services to end users. The front-end architecture is responsible for delivering the user interface and user experience (UI/UX) to the end user. While the back-end architecture is responsible for delivering the functionality, processing power, and data storage that underpins the application or service.
Front-End Architecture:
The Front-End Architecture is part of the cloud computing architecture visible to the end user. It includes the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) components. These components enable the end-user to interact with the application or service. The front-end architecture typically consists of web browsers, mobile devices, and other client-side components that communicate with the back-end architecture to deliver content and services to the user. The front-end architecture must be designed to be intuitive and easy to use. It is critical in shaping the user’s perception of the application or service.
Back-End Architecture:
Back-End Architecture is part of the cloud computing architecture that is not visible to the end user. It includes the server-side components that provide the functionality, processing power, and data storage that underpin the application or service. The Back-End Architecture typically consists of databases, servers, APIs, and other infrastructure components that communicate with the front-end architecture to deliver content and services to the user. The Back-End Architecture must be designed to be scalable, secure, and reliable. It manages and stores critical data and processes user requests in real-time.
Front-End and Back-End Communication:
The Front-End and Back-End Architectures communicate through APIs. This communication between them enables data to be passed between the two components in real time. This communication is essential to the functioning of the application or service. It enables the front end to send user requests to the back end. And the back end responds to the front end with the appropriate data or functionality. The communication between the Front-End and Back-End Architectures must be designed to be efficient and secure. It should ensure that the application or service functions correctly and data is protected.
In all, Front-End and Back-End Architectures are two critical components of cloud computing architecture that work together to deliver applications and services to end users. The front-end architecture is responsible for delivering the user interface and user experience. While the back-end architecture is responsible for delivering the functionality, processing power, and data storage. Effective communication between the two architectures is essential to the successful functioning of the application or service.
Cloud Computing Layers (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS):
Cloud computing is typically divided into three main layers: Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). Each layer provides different levels of abstraction and functionality. And the customers can choose the layer that best suits their needs.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS):
IaaS is the lowest layer in the cloud computing stack. It provides customers with access to virtualized computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking infrastructure. With IaaS, customers can rent computing resources on a pay-per-use basis. And they have full control over the virtual machines and infrastructure they use. This layer is particularly useful for customers who need complete control over their computing environment that includes the operating system and applications that run on it.
IaaS providers typically offer a variety of virtualization technologies. It includes hypervisors, containers, and bare metal servers. Popular IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and DigitalOcean.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS):
PaaS is the middle layer in the cloud computing stack. It provides customers with a platform to develop, deploy, and manage their applications. With PaaS, customers can focus on developing their applications without worrying about managing the underlying infrastructure. PaaS providers offer various services, including application development frameworks, databases, middleware, and operating systems.
And, PaaS is particularly useful for customers who want to develop and deploy applications quickly and efficiently without managing the underlying infrastructure. In addition, PaaS providers offer pre-built components and services, such as databases, message queues, and caching systems, that customers can use to build their applications. Popular PaaS providers include Heroku, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Microsoft Azure App Service, and Google App Engine.
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS):
SaaS is the top layer in the cloud computing stack. It provides customers with access to pre-built applications that are hosted in the cloud. With SaaS, customers can use applications such as email, CRM, and HR software without installing or managing the software themselves. SaaS providers manage the underlying infrastructure and ensure that the applications are available and performant.
It is particularly useful for customers who need access to business applications but do not want to invest in the infrastructure required to host and manage them. And, SaaS providers offer various applications, including email, CRM, HR, project management, and accounting software.
Popular SaaS providers include Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, Google Workspace, and Dropbox.
In all, the cloud computing stack consists of three layers: Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). Each layer provides a different level of abstraction and functionality. And the customers can choose the layer that best suits their needs. IaaS provides virtualized computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking infrastructure. PaaS provides a platform for developing, deploying, and managing applications. SaaS provides pre-built applications hosted in the cloud and accessible through a web browser.
Cloud Computing Infrastructure
Cloud Computing Infrastructure refers to the physical and virtual resources that are necessary to support computing services. This infrastructure includes data centers, servers, storage devices, network equipment, virtualization software, and other technologies required to deliver cloud computing services.
Key components of Cloud Computing Infrastructure:
Data Centers: Data centers are facilities used to house the computing resources used to deliver cloud computing services. Data centers are equipped with servers, storage devices, networking equipment, and other hardware that are necessary to provide cloud services. They are also designed to provide high availability, redundancy, and security.
Servers: Cloud computing servers are physical machines used to run virtual machines, containers, or bare-metal instances. They are optimized for scalability, reliability, and performance. Cloud servers are typically managed by the cloud provider. And it is dynamically allocated to meet changing demand.
Storage Devices: Cloud storage devices are used to store data that is accessed by cloud computing services. They can be physical devices, such as hard drives or solid-state drives, or they can be virtual devices that are accessed through the cloud infrastructure. Cloud storage devices are designed to provide high availability, durability, and scalability.
Networking Equipment: Networking equipment includes routers, switches, load balancers, firewalls, and other devices that connect cloud computing services to the internet or other networks. Networking equipment provides high performance, reliability, and security.
Virtualization Software: Virtualization software creates virtual machines, containers, or bare-metal instances that run on cloud servers. It enables the cloud provider to allocate computing resources dynamically. And it helps to isolate different cloud services from each other.
Management Tools: Cloud computing infrastructure requires advanced management tools to monitor, control, and optimize cloud services. These tools include dashboards, analytics, automation, and orchestration tools.
Cloud computing infrastructure is provided by public cloud providers, private cloud providers, or a combination of both. Public cloud providers offer cloud infrastructure as a service (IaaS). The private cloud providers offer cloud infrastructure that is dedicated to a single organization. Hybrid clouds combine both public and private cloud infrastructure to enable organizations to take advantage of the benefits of both.
Security and Privacy in Cloud Computing:
Security and privacy are two critical concerns in cloud computing. Cloud services involve storing and processing sensitive data outside of an organization’s direct control. Here are some of the key security and privacy considerations in cloud computing:
Data Privacy:
Organizations must ensure that the data they store and process in the cloud is protected from unauthorized access and use. This is achieved through various measures, such as encryption, access controls, and data masking.
Data Security:
Cloud service providers must have robust security measures in place to protect against cyber threats, such as malware, hacking, and data breaches. Security measures include firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and regular security audits.
Identity and Access Management:
Cloud providers must have strong authentication and authorization mechanisms to ensure that only authorized individuals can access cloud services and data. This may include multi-factor authentication, access control policies, and identity and access management (IAM) systems.
Compliance and Regulations:
Cloud providers must comply with various regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Cloud customers must ensure that the cloud provider they choose meets all necessary compliance requirements.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs):
Cloud customers must carefully review and negotiate SLAs with cloud providers to ensure that their security and privacy requirements are met. SLAs should include provisions for data security, privacy, and disaster recovery.
Data Sovereignty:
Data privacy laws and regulations can vary by jurisdiction. Therefore, Organizations must consider where their data is stored and processed in the cloud. Organizations must ensure that their data is stored and processed in a way that complies with all applicable regulations.
Employee Awareness and Training:
Organizations must train their employees on the security and privacy risks associated with cloud computing. And they need to provide them with guidelines and best practices for using cloud services securely.
Overall, ensuring security and privacy in cloud computing requires a shared responsibility between cloud providers and their customers. Cloud providers must provide robust security measures and comply with regulations. And cloud customers must carefully review and negotiate SLAs and implement appropriate security and privacy controls.
Risks and Threats in Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing has become a popular option for organizations to store and process their data due to its scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. However, there are also risks and threats associated with cloud computing that organizations should be aware of.
Here are some of the key risks and threats in cloud computing:
Data breaches:
One of the biggest risks in cloud computing is the potential for data breaches. Data Breaches can result in sensitive data being exposed or stolen. It can happen due to weak security controls, insider threats, or cyberattacks.
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks:
DoS attacks can overload cloud servers and cause services to become unavailable, disrupting business operations. These attacks can happen due to malicious acts or unintentional overuse of cloud resources.
Malware and Viruses:
Malware and viruses can infect cloud resources and cause data loss, theft, or corruption. These threats are introduced through email attachments, infected software, or other means.
Insider Threats:
Insiders, such as employees or contractors, can pose a threat to cloud security if they misuse their access to cloud resources. It includes intentional or unintentional data breaches, theft of intellectual property, or other malicious activities.
Third-Party Risks:
Cloud providers often rely on third-party vendors for services such as data storage, network connectivity, and software development. These third-party vendors may also be vulnerable to security risks. It can ultimately affect the security of cloud resources.
Compliance and Regulatory Risks:
Cloud providers must comply with various regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Organizations that use cloud services must ensure that their cloud providers comply with all necessary regulations to avoid compliance and regulatory risks.
Data Loss:
Data loss can occur due to various reasons, such as hardware failures, software glitches, or human errors. Organizations should have appropriate data backup and recovery mechanisms to minimize the data loss risk.
Service Disruptions:
Cloud services can experience disruptions due to various reasons, such as natural disasters, power outages, or cyberattacks. Businesses should have appropriate disaster recovery mechanisms in place to ensure business continuity.
Organizations should implement appropriate security and privacy controls, such as access controls, encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits to mitigate these risks and threats. They should also carefully review and negotiate SLAs with cloud providers to ensure that their security and privacy requirements are met. Additionally, organizations should train their employees on cloud security best practices and conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats.
Cloud Computing Security Standards:
Cloud computing security standards are sets of guidelines and best practices for securing cloud environments. These standards help organizations to ensure that their cloud providers have implemented appropriate security controls to protect their data and systems.
Here are some of the most important cloud computing security standards:
ISO/IEC 27001:
It is a widely recognized standard for information security management. It provides a framework for implementing and maintaining an information security management system (ISMS). And it covers all aspects of information security that includes cloud computing.
NIST SP 800-53:
It is a set of guidelines for security and privacy controls for federal information systems and organizations. It includes specific controls for cloud computing and is widely adopted by public and private organizations.
SOC 2:
This is a standard for auditing and reporting on the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of cloud service providers. It provides assurance that cloud providers have appropriate controls in place to protect customer data.
PCI DSS:
It is a standard for securing payment card data and applies to organizations that process, store, or transmit payment card data. Cloud providers, who handle payment card data, must comply with PCI DSS.
HIPAA:
This is a set of regulations that govern the security and privacy of healthcare data. Cloud providers who handle protected health information (PHI) must comply with HIPAA.
GDPR:
It is a regulation that governs the protection of the personal data of European Union (EU) citizens. Cloud providers who handle EU citizen data must comply with GDPR.
FIPS 140-2:
It is a standard for cryptographic modules used by federal agencies and other organizations that handle sensitive data. Cloud providers that use cryptographic modules must comply with FIPS 140-2.
These standards provide a framework for organizations to evaluate the security of cloud providers. And it ensures that their data is protected. Organizations should carefully review and negotiate SLAs with cloud providers to ensure that they comply with the necessary security standards. Additionally, organizations should conduct regular audits and assessments to ensure that their cloud providers are meeting their security requirements.
Cloud Computing Compliance Standards:
Cloud computing compliance standards refer to a set of regulations and guidelines that organizations must adhere to when using cloud computing services. These standards help ensure that cloud providers and their customers comply with legal, regulatory, and contractual obligations related to data protection, privacy, security, and other related issues.
Here are some of the most important cloud computing compliance standards:
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR):
It is a regulation that governs the protection of the personal data of European Union (EU) citizens. It applies to all organizations, regardless of where they are located, that handle the personal data of EU citizens. GDPR requires organizations to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect personal data and provides EU citizens with certain rights regarding their personal data.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA):
This set of regulations governs the security and privacy of healthcare data in the United States. It applies to healthcare providers, health plans, healthcare clearinghouses, and their business associates. HIPAA requires covered entities and business associates to implement appropriate safeguards to protect PHI.
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS):
It is a standard for securing payment card data and applies to organizations that process, store, or transmit payment card data. It requires organizations to implement a set of security controls to protect payment card data.
Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP):
It is a government-wide program that provides a standardized approach to security assessment, authorization, and continuous monitoring for cloud services. FedRAMP applies to cloud service providers that offer services to federal agencies and requires them to undergo a rigorous security assessment process.
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 27001:
This is a widely recognized standard for information security management. It provides a framework for implementing and maintaining an information security management system (ISMS). And it covers all aspects of information security that, includes cloud computing.
Service Organization Control (SOC) 2:
It is a standard for auditing and reporting on the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of cloud service providers. It is designed to provide assurance that cloud providers have appropriate controls in place to protect customer data.
Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM):
It is a framework for assessing the security of cloud providers. It provides a set of security controls and best practices that cloud providers can implement to protect customer data.
These compliance standards help organizations ensure that their cloud providers are complying with necessary regulations and guidelines related to data protection, privacy, and security. Organizations should carefully review their cloud providers’ compliance with these standards and negotiate SLAs to ensure that their data is protected. Additionally, organizations should conduct regular audits and assessments to ensure that their cloud providers are meeting their compliance requirements.
Cloud Computing Privacy Concerns:
Cloud computing offers a wide range of benefits, such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, and agility. However, these benefits come with various concerns about data privacy, security, and compliance.
Here are some of the main privacy concerns associated with cloud computing:
Data Privacy:
When organizations move their data to the cloud, they often lose control over the physical location of their data. Its lack of control can make it challenging to ensure that data is being handled and stored in compliance with privacy regulations.
Data Protection:
The data stored in the cloud is vulnerable to data breaches and cyber attacks, which can compromise user data privacy. Cloud providers must have effective data protection measures in place to protect against data breaches and ensure data privacy.
Data Ownership:
When data is stored in the cloud, it is very challenging to determine who owns the data. The ownership of data is critical for compliance with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Therefore, cloud providers must provide clear policies on data ownership and use.
Data Access:
The cloud service provider can access the data stored in the cloud. And they can access the data to provide support or troubleshooting services. It is essential to ensure that the provider has proper access controls and data management policies in place.
Data Residency:
Data residency refers to the requirement that data should be stored within a specific geographical location. Cloud providers store data in multiple locations, making it challenging to ensure compliance with data residency requirements.
To address these concerns, cloud providers must have appropriate privacy policies and procedures in place. They must comply with industry standards and regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. Cloud providers must also provide transparent information on their privacy policies, data handling practices, and data management processes. Additionally, organizations must implement security and compliance controls that work in tandem with cloud providers to ensure data privacy and security.
Cloud Computing Providers:
Cloud computing providers are companies that offer cloud-based services to organizations and individuals. These services typically include infrastructure, platform, and software solutions enabling users to access internet computing resources. It has become an integral part of modern IT infrastructure. And the market is dominated by a few major cloud computing providers.
Here are some of the main cloud computing providers:
Amazon Web Services (AWS):
AWS is a subsidiary of Amazon.com. And it is the largest provider of cloud computing services. AWS offers a broad range of services, such as infrastructure, platform, and software as service solutions. Some of their services are Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3), and Amazon RDS for relational databases.
Microsoft Azure:
Azure is a cloud computing platform developed by Microsoft. It offers various services, such as virtual machines, storage, analytics, and machine learning. Azure is well-suited for enterprise customers. And it offers services such as Azure Active Directory, Azure Virtual Machines, and Azure Kubernetes Service.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
GCP is a suite of cloud computing services developed by Google. It offers a wide range of services, including computing, storage, and networking. GCP is well-suited for data-intensive applications. It offers services like Google BigQuery, Kubernetes Engine, and Google Cloud Storage.
IBM Cloud:
IBM Cloud is a suite of cloud computing services developed by IBM. It offers various services, such as infrastructure, platform, and software solutions. IBM Cloud is well-suited for enterprise customers. It offers services such as IBM Cloud Virtual Servers, IBM Cloud Kubernetes Service, and IBM Cloud Object Storage.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI):
OCI also is a suite of cloud computing services developed by Oracle. It offers a broad range of services, including infrastructure, platform, and software solutions. OCI is well-suited for enterprise customers. It offers services such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Block Volumes, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Load Balancing.
Alibaba Cloud:
Alibaba Cloud is another cloud computing platform developed by Alibaba Group. It offers various services, such as infrastructure, platform, and software solutions. Alibaba Cloud is well-suited for customers in the Asia-Pacific region. It offers services such as Elastic Compute Service, Object Storage Service, and Relational Database Service.
When selecting a cloud computing provider, organizations should consider several factors. They must look into the provider’s reputation, service-level agreements (SLAs), pricing, and security and compliance capabilities. Organizations should also evaluate the provider’s scalability, flexibility, and ease of use. Additionally, it is essential to consider the provider’s support and training services to ensure that users can effectively utilize the cloud-based services.
Additionally, organizations should evaluate each provider’s strengths and weaknesses while selecting a cloud computing provider. It is also essential to consider how each provider’s services align with the organization’s specific needs and requirements.
Comparison of Cloud Computing Providers:
It has become an essential part of every modern business and organization. Various providers offer cloud services to customers. The leading cloud computing providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IBM Cloud, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
The following is a detailed comparison of these cloud computing providers based on various factors:
Compute Services:
AWS, Azure, and GCP offer similar compute services like Virtual Machines (VMs), Containers, and Serverless computing. They also provide Auto-Scaling, Load Balancing, and Auto-Healing services. IBM Cloud offers the same services but with limited options. OCI provides similar services but with an additional service called Bare Metal Instance. Bare Metal Instance enables customers to access and control physical servers.
Storage Services:
All major cloud providers offer similar storage services, such as Block Storage, Object Storage, and File Storage. AWS offers Amazon S3, EBS, and EFS, while Azure offers Azure Blob, Azure Disk, and Azure Files. GCP provides Cloud Storage, Cloud Block Storage, and Cloud Filestore. IBM Cloud has IBM Cloud Object Storage, IBM Cloud Block Storage, and IBM Cloud File Storage. OCI offers Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Block Volume, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage.
Networking:
All cloud providers offer Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). VPC allows customers to create and manage their private networks. AWS has Amazon VPC, Azure has Azure Virtual Network, and GCP has Google VPC. IBM Cloud offers IBM Cloud Virtual Private Cloud, and OCI has Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Virtual Cloud Network. All providers offer Load Balancers, DNS services, and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs).
Database Services:
AWS, Azure, and GCP provide similar database services such as Relational Database Service (RDS), Aurora, SQL Database, and Cloud SQL. IBM Cloud has IBM Cloud Databases for PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB, and EnterpriseDB. OCI provides Oracle Database Cloud Service, Autonomous Data Warehouse, and Autonomous Transaction Processing.
Security:
All cloud providers offer security services such as Identity and Access Management (IAM), Firewall, and Encryption. AWS has AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF), and AWS Key Management Service (KMS). Azure has Azure Active Directory, Azure Firewall, and Azure Key Vault. GCP has Google Cloud Identity and Access Management, Cloud Armor, and Cloud KMS. IBM Cloud has IBM Cloud Identity and Access Management and IBM Cloud Security Groups. OCI provides Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management, Network Security Groups, and Key Management.
AI and Machine Learning:
AWS, Azure, and GCP offer various AI and Machine Learning services such as Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing, and Computer Vision. IBM Cloud has Watson Services, which includes Watson Studio, Watson Machine Learning, and Watson Language Translator. OCI provides Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Data Science and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Data Flow.
Pricing:
Pricing varies across cloud providers. Customers should consider the cost of services while choosing a provider. AWS, Azure, and GCP have pay-as-you-go pricing models, where customers pay for what they use. IBM Cloud provides pay-as-you-go and monthly pricing models, while OCI provides hourly and monthly billing.
Overall, while all major cloud providers offer similar services, customers should choose a provider based on their specific needs and requirements.
Choosing a Cloud Computing Provider:
Choosing the right cloud computing provider is critical for businesses and organizations. There are so many options available in the market. Understanding the factors that should be considered while selecting a cloud provider is essential.
Here are some of the key factors to consider:
Cost:
Cost is one of the most crucial factors to consider while selecting a cloud provider. It is essential to evaluate the pricing models that include pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and spot instances to determine the most cost-effective option.
Security:
Security is a critical factor when it comes to selecting a cloud provider. Businesses must evaluate the provider’s security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption. The customer needs to ensure that their data is well protected.
Reliability:
Cloud providers must provide reliable services with high uptime and minimal downtime. It is essential to evaluate the provider’s service level agreement (SLA) and their track record in providing reliable services.
Performance:
Performance is another critical factor to consider when selecting a cloud provider. Businesses must evaluate the provider’s network infrastructure, which includes the number of data centers, the geographic location of data centers, and the network bandwidth.
Scalability:
Scalability is an important consideration as businesses must be able to scale their resources up or down as per their requirements and demand. The cloud provider must offer flexible scalability options. The service must have the ability to add or remove resources quickly.
Support:
The cloud provider must offer excellent customer support, including 24/7 technical support, email and phone support, and access to a knowledge base.
Compliance:
Compliance with industry-specific regulations is crucial when selecting a cloud provider. It is essential to evaluate the provider’s compliance certifications, including HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOC 2. Customers must ensure that they meet the regulatory requirements.
Integration:
The cloud provider must offer integration with the business’s existing systems and applications. It is essential to evaluate the provider’s APIs and integration capabilities.
Migration:
Migration to the cloud is a complex process. Therefore the cloud provider must offer support for migration that includes tools and documentation to make the process easier.
Reputation:
Finally, the reputation of the cloud provider is an essential factor to consider. Businesses must evaluate the provider’s track record and customer feedback to ensure that they are reliable and trustworthy.
Choosing the right cloud provider requires careful consideration of several factors that includes cost, security, reliability, performance, scalability, support, compliance, integration, migration, and reputation. By evaluating all these factors and selecting a provider that meets the business’s specific needs. So that organizations can harness the power of the cloud to drive growth and innovation.
Future of Cloud Computing:
The future of cloud computing appears to be more bright, with continued growth and expansion in the coming years.
Following are some key trends and developments to watch for:
Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud:
As organizations seek to optimize their cloud environments further, there is likely to be an increase in multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies. It involves using a combination of public, private, and/or on-premises cloud environments to meet specific business needs.
Edge Computing:
With the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and other smart technologies, there is an increasing need for computing power at the network’s edge. In Edge computing, data processing happens closer to the source rather than sending it all to the cloud for analysis.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
As AI and ML continue to transform various industries, there will be a growing need for cloud-based infrastructure to support these technologies. Cloud providers are already offering AI and ML services. AI and ML will be major growth areas in the coming years.
Serverless Computing:
Serverless computing is a model in which cloud providers manage the infrastructure needed to run applications. And they allow developers to focus on writing code. It is expected to gain traction in the coming years as organizations look to reduce costs and increase agility.
Containerization:
Containerization involves packaging applications and their dependencies in containers. It is deployed across different cloud environments. It offers greater flexibility and portability. Containerization is expected to become increasingly important as organizations adopt multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies.
Security and Privacy:
As cloud computing continues to be adopted by more organizations, there will be an increasing focus on security and privacy. Cloud providers will invest more in security measures and compliance standards to maintain customer trust.
Sustainability:
With the growing concern around climate change and carbon emissions, there is likely to be an increased focus on sustainability in cloud computing. Cloud providers are already taking steps to reduce their carbon footprint. And it is expected to become a major selling point in the coming years.
Therefore, the future of cloud computing is likely to be shaped by trends such as multi-cloud and hybrid cloud, edge computing, AI and ML, serverless computing, containerization, security and privacy, and sustainability. As organizations continue to seek new ways to optimize their cloud environments, there will be continued growth and innovation in this field.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing has been rapidly evolving over the past few years. There are several emerging trends that are expected to shape its future.
Here are some of the most important trends in cloud computing:
Edge computing:
Edge computing is a distributed computing model that brings data processing and storage closer to the devices where data is being generated. This approach helps to reduce latency and improve performance by minimizing the distance that data needs to travel. As more and more devices become connected to the internet, edge computing is becoming crucial.
Serverless Computing:
Serverless computing, which is also known as Function-as-a-Service (FaaS), is a cloud computing model in which the cloud provider manages the infrastructure required to run code. It means that developers can focus on writing code without having to worry about managing servers or infrastructure. Serverless computing is becoming more popular because it is cost-effective, flexible, and scalable.
Hybrid cloud:
Hybrid cloud is a cloud computing model that combines public and private clouds. It allows organizations to leverage the benefits of both types of clouds. It provides greater flexibility and control over their data and applications. Hybrid cloud is becoming more popular as organizations look to balance the benefits of public and private clouds.
Multi-cloud:
Multi-cloud is a cloud computing model in which an organization uses multiple cloud providers to meet its computing needs. This approach helps to prevent vendor lock-in. And it provides greater flexibility and scalability. As more cloud providers enter the market, multi-cloud is becoming more popular.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
Artificial intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are becoming increasingly important in cloud computing. Cloud providers are offering a range of AI and ML services. That is used to develop and deploy intelligent applications. These services include natural language processing, image recognition, and predictive analytics.
Containerization:
Containerization is a technology that allows developers to package an application and its dependencies into a single container that is deployed on any infrastructure. This approach helps to improve application portability and scalability. Containers are becoming more popular in cloud computing because they allow developers to build and deploy applications more quickly and easily.
Quantum Computing:
Quantum computing is a new computing paradigm that is based on quantum mechanics. It has the potential to revolutionize computing by providing exponentially faster processing speeds. Quantum Computing is still in its early stages. So, it is expected to become increasingly important in cloud computing as more quantum computing technologies become available.
The discussed above are some of the emerging trends in cloud computing that are likely to shape its future. Organizations that are looking to take advantage of cloud computing should consider these trends when planning their cloud strategies.
Impact of Cloud Computing on Businesses and Industries:
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate by offering significant benefits in terms of cost savings, agility, scalability, and efficiency.
Here are some of the major impacts of it on businesses and industries:
Cost Savings:
It allows businesses to reduce their IT infrastructure and maintenance costs significantly. Businesses can pay for only the required services and avoid upfront costs for hardware, software, and maintenance.
Increased Agility:
Cloud computing enables businesses to scale their resources up or down to meet changing business demands. It allows businesses to respond more quickly to market changes and customer demands.
Enhanced Collaboration:
It provides businesses with tools and platforms that enable employees to collaborate and work together more effectively. It increases productivity and better business outcomes.
Improved Data Security:
Cloud computing providers offer advanced security features and technologies to help businesses protect their data from theft, loss, or damage. It is important for businesses that deal with sensitive customer data, such as financial or healthcare information.
Access to Advanced Technologies:
Cloud computing providers offer access to advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics. It would be difficult or costly for businesses to implement it on their own.
Increased Innovation:
It allows businesses to experiment and try new ideas without significant upfront investment. This encourages innovation and leads to new products, services, and business models.
Cloud computing has impacted various industries in different ways.
Healthcare: It enables healthcare providers to store, share, and analyze large amounts of patient data securely and cost-effectively. It leads to better patient outcomes, reduced costs, and improved accessto care.
Finance:
Cloud computing helps financial institutions to process transactions faster, improve customer experience, and reduce fraud. It has also supported financial institutions to provide innovative services such as mobile banking and digital payments.
Education:
It allows educational institutions to provide online learning platforms and resources. It makes education more accessible and affordable for students. In addition, it also has supportive and collaborative research and data sharing between institutions.
Retail:
Cloud computing helps retailers to offer personalized and engaging customer experiences across various channels, such as online, mobile, and in-store. It supports retailers in optimizing inventory management, logistics, and supply chain operations.
Manufacturing:
Cloud computing supports manufacturers in improving supply chain visibility, optimizing production processes, and reducing costs. It also helps manufacturers to leverage advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and predictive analytics to improve product quality and performance.
It has transformed how businesses operate and enable them to become more efficient, agile, and innovative. As cloud computing continues to evolve, businesses and industries will continue to benefit from its numerous opportunities.
Challenges and Opportunities in Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses and organizations operate by offering various benefits such as cost savings, scalability, agility, and increased productivity. However, it also presents a number of challenges and opportunities that must be taken into consideration. In this section, we will discuss the major challenges and opportunities that come with cloud computing.
Challenges:
Security and Privacy: One of the biggest challenges of cloud computing is security and privacy. With data stored in the cloud, there is always a risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. Cloud service providers must implement security measures such as encryption, access controls, and firewalls to mitigate these risks.
Compliance: Compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS is another challenge that businesses must face when using cloud computing. Businesses must ensure that their cloud provider is compliant with these regulations to avoid any legal repercussions.
Vendor Lock-In: Vendor lock-in is a situation where a business becomes dependent on a particular cloud provider’s services and cannot easily switch to another provider. Businesses must ensure that their cloud provider offers a flexible service that allows them to migrate to another provider if necessary.
Downtime: Cloud service providers can experience downtime due to various reasons, such as maintenance, upgrades, and power outages. Businesses must ensure that their cloud provider offers reliable services with minimal downtime.
Opportunities:
Cost Savings: Cloud computing offers significant cost savings for businesses by eliminating the need for expensive hardware and software. Cloud service providers offer pay-as-you-go pricing models. It allows businesses to only pay for what they use.
Scalability: Cloud computing offers unparalleled scalability. And it allows businesses to easily increase or decrease their computing resources based on their needs. It helps businesses to avoid over-provisioning or under-provisioning their resources.
Collaboration: Cloud computing enables collaboration among teams and organizations regardless of their physical location. This allows for faster and more efficient communication and collaboration among employees.
Innovation: Cloud computing allows businesses to innovate and experiment with new technologies without incurring significant costs. Businesses can quickly test and deploy new applications, services, and features in the cloud.
In all, cloud computing offers significant benefits to businesses and organizations. But it also presents several challenges and opportunities that must be considered. Businesses must carefully evaluate their needs and choose a cloud provider with the necessary features and services to meet them.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations:
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate. It provides numerous benefits, such as reduced costs, increased scalability, and flexibility. And it improves collaboration and productivity. However, it also poses several challenges, including security and privacy concerns, compliance issues, and vendor lock-in.
Therefore, businesses must carefully evaluate their needs and choose a cloud computing provider that aligns with their requirements, budget, and business goals. They should also consider the provider’s security and privacy standards and compliance certifications.
Moreover, businesses should also be aware of emerging trends and new technologies in cloud computing, such as edge computing, serverless computing, and containerization, offering new opportunities for innovation and efficiency.
In conclusion, cloud computing is a rapidly evolving technology offering numerous business benefits. But it also poses several challenges. By carefully evaluating their needs, choosing the right provider, and staying up to date with emerging trends and technologies, businesses can leverage the full potential of cloud computing and stay ahead in today’s digital age.